This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.
One day your beard looks full and even—the next, you’re staring at a smooth, coin-sized bald spot along your jawline. Alopecia barbae doesn’t announce itself with warning signs or gradual thinning. This autoimmune condition attacks beard follicles with sudden precision, leaving circular patches that can shake your confidence and trigger a flood of questions.
The good news? Your follicles aren’t dead. While your immune system has temporarily turned against them, medical treatments ranging from corticosteroids to JAK inhibitors can halt the attack and coax hair back. Understanding what triggers these patches and which interventions work fastest puts you back in control of your beard’s future.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Alopecia Barbae in Beards?
- What Causes Alopecia in The Beard?
- How to Identify Beard Alopecia Symptoms
- How is Alopecia Barbae Diagnosed?
- What Are The Best Treatments for Beard Alopecia?
- Can You Regrow Beard Hair After Alopecia?
- How to Prevent and Manage Beard Alopecia
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can you grow a beard with alopecia?
- What causes alopecia in the male beard?
- How do you treat facial hair alopecia?
- How do you treat beard alopecia areata?
- What is the remedy for male alopecia?
- What causes beard alopecia?
- Can alopecia cause beard hair loss?
- Can you cure beard alopecia?
- Will my beard grow back after alopecia?
- Is there a way to fix bald spots in a beard?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Alopecia barbae is an autoimmune condition that causes sudden, circular bald patches in your beard, but your hair follicles aren’t permanently destroyed—regrowth is possible with the right medical intervention.
- Corticosteroids, JAK inhibitors, and immunotherapy are proven treatments that halt the immune attack on your follicles, with most men seeing initial regrowth within 3-6 months if they stay consistent.
- The condition stems from your immune system mistaking beard follicles for threats, often triggered by stress, viral infections, or genetic predisposition—especially if you have a family history of autoimmune disorders.
- Beyond medical treatment, managing stress through daily meditation, maintaining 7-9 hours of sleep, and optimizing nutrition with protein, biotin, and omega-3s significantly improves your chances of full beard restoration.
What is Alopecia Barbae in Beards?
If you’ve noticed smooth, round bald spots appearing in your beard, you’re likely dealing with alopecia barbae. This autoimmune condition specifically targets facial hair follicles, causing sudden and unpredictable hair loss that can shake your confidence.
Fortunately, there are proven strategies to fix bald spots in your beard that address both alopecia barbae and other common causes of patchy growth.
Understanding what sets this condition apart from regular hair loss is your first step toward taking control and finding the right treatment.
Definition and Overview
Alopecia barbae is an autoimmune condition that attacks your beard hair follicles, causing patchy hair loss limited to your facial hair. It’s a form of alopecia areata that disrupts normal beard health, triggering sudden bald spots—usually smooth, round patches along your jawline.
While autoimmune factors drive this hair loss, the good news is regrowth options exist, and your follicles aren’t permanently destroyed. For a deeper look at the immune system response involved, see this authoritative resource.
How It Differs From Other Hair Loss
Unlike other hair loss conditions, alopecia barbae zeroes in exclusively on your facial hair follicles, creating distinct circular or irregular bald patches in your beard rather than diffuse thinning. This autoimmune condition triggers patchy alopecia through immune cells attacking beard hair roots—not hormonal shifts or genetic balding patterns.
Here’s what sets beard hair loss apart:
- Localized autoimmune attack: Your immune system targets facial follicles specifically, leaving scalp hair untouched in many cases
- Exclamation mark hairs: Broken hairs taper near the scalp, a hallmark absent in androgenic hair loss
- Spontaneous regrowth potential: Unlike permanent hair follicle damage from scarring conditions, beard regrowth remains possible even without treatment
Notably, can help distinguish beard-specific hair loss from more common hereditary patterns.
Prevalence in Men
Understanding how often this autoimmune condition strikes can help you contextualize your experience. Beard hair loss affects several percent of adult males, with prevalence varying by population and diagnostic criteria.
| Factor | Prevalence Pattern |
|---|---|
| Age factors | Most common in men aged 20s–40s |
| Ethnic variations | Rates differ across ethnic groups |
| Regional differences | Higher in areas with autoimmune disease |
| Urban prevalence | More cases reported in cities |
| Demographic trends | Increases with family history of alopecia areata |
Your risk climbs if you’ve got other autoimmune conditions or relatives with similar hair loss patterns.
What Causes Alopecia in The Beard?
You can’t fight what you don’t understand. Alopecia barbae doesn’t just happen randomly—your immune system turns against your own hair follicles, and several factors can pull that trigger.
Let’s break down what actually causes those patches to show up in your beard.
Autoimmune Triggers
Your immune system doesn’t always play by the rules—sometimes it mistakes your beard follicles for invaders and launches a full-scale attack. This autoimmune response strips away the follicle’s natural protection, allowing inflammatory T cells to swarm and shut down hair growth.
Here’s what sets off this cellular rebellion:
- Viral infections like Epstein–Barr or hepatitis can flip the immune switch
- Physical or emotional stress intensifies immune dysregulation
- Regulatory T cells fail to stop the autoreactive assault on follicles
Genetic Predisposition
Your family tree can hold clues to beard alopecia—about 10 to 20 percent of people with alopecia areata report affected relatives, compared to just 1.7 percent without the autoimmune disorder.
Genes in the HLA region shape how your immune system targets hair follicles, though inheritance patterns show that dozens of genetic markers raise risk, not one single gene.
Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Stress, sleep patterns, and nutrient deficiencies can trigger the autoimmune cascade that drives alopecia barbae. When cortisol stays elevated from chronic stress, your immune cells mistake beard follicles for foreign tissue.
You can take control with these lifestyle changes:
- Sleep 7 hours nightly in a dark, cool room
- Eat regular meals rich in protein, iron, zinc, and vitamin D
- Cut smoking and limit alcohol to protect follicle blood flow
- Practice daily relaxation techniques like breathing exercises or brisk walks
Stress management and hair growth promotion work hand in hand—men who pair medical treatments with consistent exercise often see better beard coverage within 6 to 12 months.
Associated Medical Conditions
Your body’s defense network can turn against more than just beard follicles. Men with alopecia barbae carry higher odds of thyroid issues, inflammatory bowel disease, and rheumatologic disorders—each reflecting a shared autoimmune disorder pattern that extends beyond facial hair.
| Autoimmune Disorders | Risk in Alopecia Barbae |
|---|---|
| Thyroid Issues (Hashimoto’s, Graves) | 0.6% vs 0.4% general population |
| Skin Conditions (vitiligo, psoriasis) | 1.4–2.4% vs 0.5–1.2% controls |
| Gastrointestinal Diseases (Crohn’s, celiac) | 0.5–1.3% vs 0.3–0.9% controls |
| Rheumatologic (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis) | 1.4–2.3% vs 0.4–1.3% controls |
When your immune system misfires at hair roots, it may already be targeting stomach lining, thyroid cells, or joint tissue. That’s why dermatologists screen for endocrine problems and autoimmune disease when patchy beard loss appears—catching these conditions early gives you leverage to protect both your health and your beard.
How to Identify Beard Alopecia Symptoms
Recognizing the early signs of beard alopecia puts you in control of your treatment timeline. The symptoms show up in distinct patterns that you can spot yourself, though they sometimes overlap with other skin conditions.
Here’s what to watch for on your face and jawline.
Circular Bald Patches
Circular bald patches are the hallmark sign that alopecia barbae has targeted your beard. You’ll spot smooth, coin-sized areas where hair has completely vanished, often along your jawline or chin. These patches have sharp borders that separate bare skin from your surrounding beard.
- Each patch usually starts small, around quarter-size, before potentially expanding
- Multiple circles can appear simultaneously in different beard zones
- The bald skin feels unusually smooth, like peach fuzz without any stubble
- Patches may merge over weeks, creating larger irregular areas of hair loss
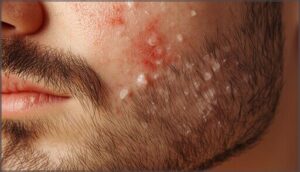
Skin Changes and Irritation
Beyond missing hair, your beard skin often rebels with visible changes that demand attention. Redness treatment becomes essential when patches turn pink or inflamed, signaling active autoimmune disease management needs. You might battle itchy skin, dry patches with flaky texture clinging to remaining hairs, or burning discomfort that flares after shaving—all signs your skin health is compromised alongside follicle function.
| Skin Change | What You’ll Notice | Why It Happens |
|---|---|---|
| Redness & Inflammation | Pink or warm patches, tender to touch | Autoimmune attack on follicles triggers local inflammation |
| Itching & Burning | Prickly sensation before hair sheds, worse at night | Irritated follicles and heightened nerve sensitivity in active alopecia areata zones |
| Dryness & Flaking | White scales, tight rough texture | Barrier breakdown plus possible seborrheic dermatitis overlap |
| Shaving Irritation | Bumps, stinging from aftershave, contact reactions | Compromised skin reacts strongly to grooming products and friction. |
Irritation management starts with switching to fragrance-free cleansers and skipping harsh alcohol toners that strip your compromised barrier. Corticosteroids prescribed by your dermatologist can calm the inflammation driving these skin changes, while gentle moisturizers restore comfort to dry, flaky areas between bald spots.
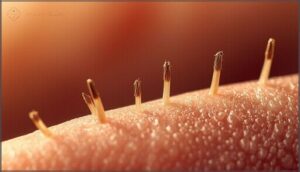
Exclamation Mark Hairs
Look closely at the border of any new bald spot—you might spot tiny broken hairs standing like miniature exclamation points.
These diagnostic markers, classic in alopecia areata and alopecia barbae, measure just 2 to 4 millimeters, thicker and darker at the tip yet narrowing near the root.
Their presence signals active autoimmune disease attacking your follicle health, distinguishing real hair loss patterns from simple shaving trauma.
Itching or Discomfort
Beyond those telltale exclamation mark hairs, many men notice mild to moderate itching days or even weeks before visible bald patches appear.
That tingling sensation—often localized to small circular zones—acts as an early warning of active alopecia areata in your beard.
Inflammation and skin irritation can follow hair loss, making the smooth bald area feel tender or rough despite its hairless appearance.
How is Alopecia Barbae Diagnosed?
Getting a proper diagnosis is the first step to taking back control of your beard health. Your dermatologist will use a combination of examination techniques and tests to confirm alopecia barbae and rule out other causes of hair loss.
Here’s what you can expect during the diagnostic process.
Dermatological Examination
Your dermatologist starts with a visual assessment, examining the beard and scalp for telltale patterns that confirm alopecia barbae. This hands-on process reveals what’s really happening beneath your skin.
- Detailed skin checks for inflammation, scaling, or discoloration around patches
- Hair evaluation to spot exclamation mark hairs and fragile shafts
- Lesion mapping with precise measurements to track progression
- Dermatoscopy to magnify follicular details invisible to the naked eye
- Diascopy testing to assess vascular involvement in affected areas
Hair Sample and Microscopy
After that visual check, your dermatologist may pluck or clip hairs for microscopy techniques that reveal autoimmune disorders at work. Sample preparation involves mounting strands to analyze hair shaft disorders and follicle structures under magnification.
Diagnostic features like exclamation mark hairs and pigment patterns confirm alopecia barbae, while hair follicle analysis distinguishes it from fungal infections or other causes of hair loss.
Blood Tests and Biopsy
Once microscopy points toward autoimmune trouble, your doctor orders a blood panel to unmask hidden culprits—thyroid disease, anemia, vitamin gaps—that fuel hair follicles’ rebellion. Skin biopsy clinches the diagnosis of alopecia barbae by revealing lymphocytes swarming your immune system’s attack zones.
Here’s what labs usually check:
- Thyroid hormone analysis to catch metabolic triggers
- Complete blood count for anemia screening
- Ferritin and vitamin levels supporting follicle health
- Autoimmune tests like ANA for systemic disorders
- Infection screening to rule out fungal mimics
Ruling Out Other Conditions
Your doctor runs infection screening through blood cultures and skin swabs to exclude bacterial folliculitis or fungal tinea barbae mimicking alopecia barbae.
Hormone tests assess thyroid function and androgens, while nutrient deficiencies like iron and vitamin D get flagged. Skin biopsy confirms this autoimmune disorder by revealing lymphocyte patterns distinct from scarring alopecias, ensuring accurate diagnosis of alopecia barbae.
What Are The Best Treatments for Beard Alopecia?
You have several proven treatment options to tackle beard alopecia head-on and reclaim control over your facial hair.
The right approach depends on your specific condition, severity, and how aggressively you want to pursue regrowth. Here’s what actually works, backed by clinical evidence and real-world results.
Topical and Oral Medications (Corticosteroids, Minoxidil, JAK Inhibitors)
In the context of Alopecia Barbae treatment, you’ve got three powerful medication options.
Corticosteroid therapy addresses inflammation by calming your overactive immune response—apply high-potency formulas like clobetasol once or twice daily. Minoxidil treatment stimulates follicles, available as topical solutions or oral tablets for resistant cases.
JAK inhibitors block inflammatory pathways, though they require careful monitoring for medication side effects. Each approach needs months to show regrowth outcomes, so consistency matters.
Immunotherapy and Other Medical Options
Beyond conventional drugs, immunotherapy harnesses your body’s own defenses to tackle beard alopecia. These sophisticated regrowth strategies include monoclonal antibodies that block follicle-damaging signals and cancer vaccines designed to retrain immune responses.
- Diphencyprone creates a controlled allergic reaction that redirects immune assault away from hair roots
- JAK inhibitors interrupt inflammation pathways, often showing visible regrowth within 4 to 6 months
- Monoclonal antibodies target specific immune triggers while preserving your broader immunity
- Treatment combinations pair immunotherapy with minoxidil or steroids for faster, more durable results
Natural Remedies and Home Care
You can fortify your beard care arsenal with natural supplements like biotin and zinc, which support hair growth from within. Pair these with gentle skin care—cleansing with mild, fragrance-free products preserves natural oils while reducing irritation around beard hair loss patches.
Add weekly beard massage using diluted rosemary or castor oil to boost circulation, creating conditions that favor hair regrowth in alopecia barbae.
Effectiveness and Timeline for Results
You won’t see overnight miracles with alopecia barbae treatment—but you’ll see results if you stay the course. Here’s what to expect:
- First signs of regrowth appear after 6 to 12 weeks of consistent therapy
- Full hair cycle completion requires 3 to 6 months for best results
- Response rates show roughly half of users experience noticeable improvement within 12 weeks
- Reassessment timing occurs at 4 to 6 months if patches haven’t responded
Can You Regrow Beard Hair After Alopecia?
Yes, you can regrow beard hair after alopecia barbae, though success varies based on the severity of your condition and how your body reacts to treatment.
Several medical techniques, nutritional strategies, and surgical options exist to help restore your facial hair. Understanding what works, what doesn’t, and what timeline to expect will help you take control of your regrowth journey.
Medical Hair Regrowth Techniques
You’ve got several powerful medical restoration options to kickstart beard regrowth. Minoxidil applied twice daily can boost hair follicle activity within four to six months. Corticosteroids reduce immune attacks on your beard.
Platelet therapy delivers concentrated growth factors directly to affected patches. JAK inhibitors reset follicle function in eight to sixteen weeks. Laser treatment stimulates dormant follicles with minimal side effects, giving you real Alopecia Barbae treatment choices.
Nutritional and Supplement Support
Medical treatments work best when you fuel your follicles from within. Vitamin therapy targets specific deficiencies—vitamin D, zinc, and iron blood tests reveal what you’re actually missing. Mineral supplements like biotin plus zinc support keratin production for stronger hair regrowth.
Here’s your nutrition game plan:
- Load up on omega-3s from salmon and flaxseeds to calm autoimmune attacks on your beard
- Balance your protein intake at 0.8 to 2.0 grams per kilogram daily for new hair building blocks
- Add probiotics like Lactobacillus rhamnosus to regulate immune responses through gut health
Dietary planning with fermented foods and fiber feeds beneficial bacteria that may reduce alopecia areata plaques. Testing before supplementing prevents toxicity and saves you from wasting money on nutrients you don’t need.
Beard Transplant and Surgical Options
When supplements don’t cut it, hair restoration offers a permanent fix.
Follicular unit extraction harvests individual grafts from your scalp donor area and places them at precise angles to match natural beard growth.
Surgical techniques require 1,000 to 3,000 grafts depending on patch size.
Transplant costs range from $3,000 to $7,000, with graft survival rates hitting 85 to 95 percent when you follow proper aftercare protocols.
Managing Expectations for Regrowth
Surgery isn’t a magic bullet—regrowth timelines for alopecia barbae demand patience. Most treatments show initial hair density improvements within three to six months, but full beard restoration often takes twelve to twenty-four months.
Treatment outcomes vary widely based on your immune response and follicle health. Set realistic patient expectations: you might see patchy regrowth before complete coverage, and some areas may never match your original thickness.
How to Prevent and Manage Beard Alopecia
You can’t always prevent alopecia barbae, but you can take control of what happens next. Managing this condition means addressing both your physical health and your mental well-being—because stress, habits, and how you care for your beard all play a role.
Here’s what you need to focus on to keep your beard in fighting shape and protect yourself from future flare-ups.
Stress Reduction Strategies
Stress doesn’t just sit in your head—it triggers immune system chaos that can worsen autoimmune disorders like alopecia barbae. Cutting stress gives you real control over hair loss progression.
The following methods can help you manage stress and its impact on hair loss:
- Mindful meditation for 10 minutes daily lowers cortisol within 2 weeks
- Breathing exercises calm your autonomic nervous system during flare-ups
- Aerobic activity 150 minutes weekly improves stress tolerance
- Consistent sleep (7–9 hours) reduces immune reactivity
- Social support through therapy or groups builds emotional balance
Beard Care and Maintenance Tips
You can’t regrow hair from damaged follicles if you’re sabotaging them daily. Proper beard care and maintenance protects vulnerable skin beneath your beard.
Wash with fragrance-free cleanser every other day, apply 3–10 drops of beard oil within one minute of drying, and exfoliate 1–2 times weekly. Brush from neck upward using boar bristles to distribute oils evenly and prevent breakage.
Lifestyle Changes for Beard Health
Your daily habits directly influence beard health tips more than you realize. Target these three areas for beard hair loss prevention and hair growth:
- Diet Planning – Consume 1.2–1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, biotin-rich foods, and omega-3s from fish to support follicle function and beard hair care.
- Stress Management – Practice 10 minutes of daily meditation and maintain an Exercise Routine with 150 minutes of cardio weekly to lower cortisol and boost circulation.
- Sleep Patterns – Aim for 7–9 hours nightly to improve hormone balance and tissue repair critical for beard care.
Emotional Support and Coping Mechanisms
Acknowledge the psychological toll that alopecia barbae and other autoimmune disease conditions place on your mental health. Seek emotional validation through therapy or support groups—active listening can reduce negative thoughts by 15 percent within a month.
Practice coping strategies like 4-7-8 breathing during self-conscious moments, and establish self-care routines that give you control. Living with alopecia areata demands resilience, not flawlessness.
Living with alopecia areata demands resilience, not flawlessness—practice coping strategies and self-care routines that give you control
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can you grow a beard with alopecia?
Can you still grow facial hair with patchy loss? Yes—many men with Alopecia Barbae see spontaneous Hair Follicle recovery and Beard Regrowth within months.
Though Alopecia Barbae treatment accelerates Regrowth Tips and improves Alopecia Management outcomes.
What causes alopecia in the male beard?
Alopecia Barbae stems from autoimmune triggers—your immune system attacks hair follicles in targeted patches.
Genetic factors, stress response, and inflammatory causes increase the risk, especially if you’ve got a family history of autoimmune disorders.
How do you treat facial hair alopecia?
Your dermatologist can prescribe topical corticosteroids or minoxidil to promote facial hair regrowth. JAK inhibitors and immunotherapy offer stronger treatment for alopecia barbae when first-line options don’t restore your beard.
How do you treat beard alopecia areata?
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket—beard alopecia areata treatment combines topical corticosteroids, minoxidil, and sometimes JAK inhibitors.
Intralesional steroid injections target stubborn patches effectively, promoting autoimmune response control and hair regrowth.
What is the remedy for male alopecia?
Male alopecia treatment includes topical corticosteroids to calm inflammation, minoxidil for beard regrowth, and JAK inhibitors for stubborn hair loss.
Combining these hair restoration methods with stress management yields the best alopecia areata outcomes.
What causes beard alopecia?
Your body’s defense system turns traitor when it targets beard follicles, causing patchy hair loss.
Autoimmune factors drive this attack, while genetic predisposition, stress response, and hormonal imbalance set the stage for beard alopecia.
Can alopecia cause beard hair loss?
Yes, alopecia barbae directly causes beard hair loss through an autoimmune attack on follicles.
Your immune system mistakenly targets hair roots in the beard, creating circular bald patches that can shift or expand unpredictably.
Can you cure beard alopecia?
There’s no permanent cure, but your beard regrowth is achievable.
Treatment options like corticosteroids and JAK inhibitors can effectively manage the autoimmune response, though hair loss may recur over time.
Will my beard grow back after alopecia?
Your beard can come back—many men see hair regrowth with treatment, though timelines vary.
Expect several months to a year for regrowth patterns to emerge as hair follicle health improves and autoimmune reactions settle.
Is there a way to fix bald spots in a beard?
You can treat bald spots in your beard using topical corticosteroids, minoxidil, or JAK inhibitors.
These options target inflammation, stimulate hair follicles, and encourage beard hair regrowth in patches affected by alopecia barbae.
Conclusion
You’re not fighting this battle blindfolded. Knowing how to fix alopecia in beard means understanding the autoimmune mechanics behind those patches and attacking them with proven medical interventions.
Corticosteroids, JAK inhibitors, and immunotherapy don’t just mask symptoms—they reprogram your immune response and restart follicle activity. Pair treatment with stress management and targeted nutrition, and you’ll stack every advantage in your favor.
Your beard’s comeback starts with informed action, not wishful waiting.
- https://www.myhair.ai/blog/beard-hair-loss-causes-tracking-solutions-2025
- https://academic.oup.com/bjd/advance-article/doi/10.1093/bjd/ljaf452/8322888
- https://www.naaf.org/navigation-toolkit/expectations-for-jak-inhibitor-treatment/
- https://aventusclinic.com/minoxidil-beard-growth/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7193229/