This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.

Knowing the difference is key to getting the right treatment.
Scabies is a skin infestation caused by a mite, while bed bugs are insects that feed on blood.
You’ll notice different symptoms, like burrows for scabies and bites for bed bugs.
Understanding the distinction between scabies vs bed bugs will help you reclaim your comfort, so let’s explore the details to get you on the path to relief and finally scratch that itch for answers.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Scabies Vs Bed Bugs
- Bed Bug Infestations
- Scabies Infestations
- Identifying Bed Bugs
- Treatment Options
- Prevention Strategies
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How do I know if I have bed bugs or scabies?
- How do I know if I have scabies or bed bugs?
- Can you see scabies on bed sheets?
- What do scabie bites look like?
- Do scabies live in mattresses?
- Are scabies more common than bed bugs?
- What are scabies and what do they look like?
- What is the difference between bed bugs and scabies mites?
- Are bed bugs harder to get rid of than scabies?
- Do bed bugs bite scabies?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- You’ll be able to identify the difference between scabies and bed bugs by looking for distinct signs, such as intense itching and burrow marks for scabies, and red welts for bed bugs.
- You can treat scabies with topical or oral medications, but bed bug infestations often require heat treatment, washing, and drying of items, or professional pest control services.
- You’ll want to practice good personal hygiene, use environmental control measures, and implement long-term prevention techniques to prevent scabies and bed bug infestations.
- You’ll find that understanding the key characteristics, symptoms, and transmission methods of scabies and bed bugs is crucial to choosing the right treatment and reclaiming your comfort.
Scabies Vs Bed Bugs
You’re likely wondering what sets scabies and bed bugs apart, and understanding their differences is vital to identify and treat them effectively.
Know the differences to effectively treat scabies and bed bugs
By knowing the key characteristics, symptoms, and transmission methods of scabies and bed bugs, you can take the first step in protecting yourself from these pesky infestations.
Physical Characteristics
You’ll notice scabies vs bed bugs differ in body shape, leg count, and color.
| Characteristic | Scabies | Bed Bugs |
|---|---|---|
| Body Shape | Round | Flat, oval |
| Leg Count | 8 | 6 |
| Color | Transparent | Brown, reddish tint |
The key differences, including body shape, are crucial for identification.
Size and Visibility
You’ll find scabies mites are microscopic, while bed bugs are visible.
Bed bugs aren’t adapted to live in hair because of their body structure preferences.
| Characteristic | Scabies | Bed Bugs |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Microscopic | 5-7mm |
| Visibility | Not visible | Visible |
| Magnification | Needed | Not needed |
| Identification | Difficult | Easier |
The key difference in visibility and size makes it easier to identify bed bugs, as they are visible to the naked eye, unlike scabies, which requires magnification.
Key Differences
You can easily tell them apart. Scabies mites are Microscopic vs. Visible; you can’t see them, unlike bed bugs.
| Feature | Scabies Mites | Bed Bugs |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Microscopic | Visible |
| Bite Markings | Rash, burrows | Raised welts |
| Transmission Method | Skin contact | Infested items |
Scabies vs bed bugs also differ in Survival Time. Scabies mites die quickly without a host. Treatment Differences are key. You need prescriptions for scabies treatment, not just creams for bed bug bites.
Bed Bug Infestations
You’re likely to encounter bed bug infestations in your home, especially if you’ve recently traveled or acquired used furniture.
As you try to identify the source of the problem, you’ll need to look for signs of bed bugs, such as small, reddish-brown insects or tiny eggs and eggshells in dark, dry areas, which can be a clear indication of a bed bug infestation.
Signs and Symptoms
You’ll experience intense itching from bed bug bites, with rash differences and distinct bite patterns.
Scabies symptoms include burrow visibility and secondary infections, causing itchy skin.
Rash identification is key to distinguishing scabies vs bed bugs, as bed bug bites often appear as red welts in a line or cluster, with rash differences and distinct bite patterns being notable.
Transmission Methods
You’ll get bed bugs through direct contact, shared items, or environmental spread.
They hitchhike on clothing, furniture, and luggage, making them infestation vectors.
Scabies, however, spreads via physical contact, highlighting different transmission methods for each pest, including contagion factors and shared items.
Bed bugs are unlikely to reside in hair, as they prefer fabric, which is a key factor in understanding their transmission methods and environmental spread.
Risk Factors
You’re at risk for bed bugs in Crowded Conditions, with Weakened Immunity, or after Travel Exposure.
Key risk factors include:
- Shared Items
- Delayed Treatment
- Close contact
- Contagious outbreaks
- Scabies or bed bug infestations, which can lead to Contagious outbreaks.
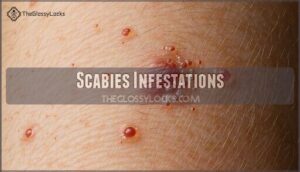
Scabies Infestations
You’re likely to experience severe itching and a rash if you have a scabies infestation.
As you learn more about scabies infestations, you’ll understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available to help you manage and eliminate the condition.
Causes and Symptoms
You’ll notice scabies causes intense itching, worsening at night, with a rash and grey-white streaks.
Initial infestation leads to symptom progression, including itch intensity and rash development, which can result in secondary infections if left untreated, similar to bed bug bites, but with distinct differences in itching and rash.
This is unlike chemical burns, which may require immediate rinsing with water, a treatment that highlights the importance of understanding the cause of the condition to apply the appropriate remedy.
Burrow Appearance
Beyond the initial symptoms, let’s look at scabies burrows. These tiny tunnels are diagnostic features.
Burrow visibility is often poor. Look for:
- Grayish-white, raised lines.
- Tunnel characteristics that are irregular.
- Burrow location in skin folds.
These burrows, created by scabies mites, cause skin reactions. They aren’t bed bug bites. You’ll find them in specific areas. Identifying these burrows is key.
Itching and Discomfort
You experience intense itching from scabies, leading to sleep disturbance and secondary infections.
| Itch intensity | Sleep disturbance | Secondary infections |
|---|---|---|
| High | Common | Possible |
| Medium | Occasional | Rare |
| Low | Uncommon | Unlikely |
Identifying Bed Bugs
You’re trying to identify bed bugs, and it’s vital to know what to look for.
You’ll need to check for small, reddish-brown, wingless insects, about the size of an apple seed, in dark, dry spaces like mattress seams, looking for complete concepts such as these insects in specific locations.
Habitat and Hiding Spots
You’ll find bed bugs in mattress seams, furniture cracks, and seams of chairs and couches, where they hide and feed.
They pose travel risks when sharing items, especially in cracks and folds of furniture and curtains.
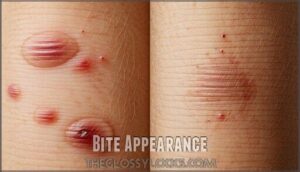
Bite Appearance
You’ll identify bed bug bites by their raised, red welts, often in a zigzag pattern.
Scabies mites cause a rash with raised lines and intense itching.
Bite appearance and distribution vary, with bed bug bites typically on exposed skin and scabies in skin folds, causing distinct rash morphology.
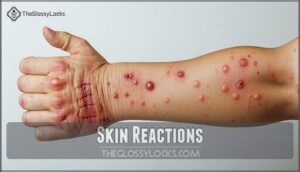
Skin Reactions
You’ll notice skin reactions to bed bug bites, including itching, rash, and skin irritation.
Bite appearance can vary, but often appears as red, flat welts.
Itch intensity can lead to secondary infections or allergic reactions if left untreated, causing further skin discomfort and potentially severe rash differences.
Treatment Options
You’ll need to evaluate different treatment options for scabies and bed bugs, as they require distinct approaches.
You can treat scabies with topical or oral medications, while bed bug infestations often require heat treatment, washing, and drying of items, or professional pest control services, which are complete concepts in managing these pests.
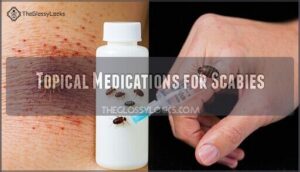
Topical Medications for Scabies
You’ll use topical medications for scabies, including:
- Permethrin cream
- Sulfur cream
- Crotamiton lotion
- Lindane, with concerns about resistance management and skin application techniques, considering permethrin effectiveness and prescription medication guidelines.
You can find various permethrin creams online, which is useful for managing scabies treatment.
Oral Medications for Scabies
You’ll take oral ivermectin, a prescription medication, to treat scabies.
Ivermectin dosage is usually 200 µg per kilogram of body weight, with one or two doses often curing the infection, offering an alternative to topical treatments with fewer side effects, especially for pediatric use.
You can find products related to ivermectin oral dosage online, which provides a convenient way to access information on oral ivermectin.
Heat Treatment for Bed Bugs
For bed bugs, heat treatment is a powerful tool. It’s a key part of pest control.
Heat effectiveness depends on reaching the right temperature thresholds. You’ll want to examine these points:
- Equipment types vary.
- Treatment duration matters.
- Safety precautions are essential.
- Professional pest control guarantees success.
Remember, heat treatment targets bed bugs directly. Consider using specialized heating equipment for superior results. This differs greatly from scabies treatment.
Always prioritize safety. With the right approach, you can win against bed bugs.
Prevention Strategies
You can prevent scabies and bed bug infestations by taking a few simple steps.
By practicing good personal hygiene, using environmental control measures, and implementing long-term prevention techniques, you can reduce your risk of getting these pests.
This approach allows for effective prevention and control of scabies and bed bug infestations.
Personal Hygiene Practices
To prevent scabies and bed bugs, practice regular showers, hand washing, and nail hygiene.
Maintain clothing cleanliness, and avoid sharing personal items to reduce the risk of itching, rash, and infestation, as shared items can spread scabies and bed bugs easily.
Remember to protect your skin by using broad-spectrum sunscreen daily to ensure complete skin protection and prevent skin issues, which is a key part of overall hygiene.
Environmental Control Measures
You’ll want to focus on environmental control measures.
Consider:
- Vacuuming techniques
- Furniture treatment
- Temperature control to prevent infestations, ensuring home sanitation practices and pest control methods are in place for preventative cleaning and laundry protocols.
Long-term Prevention Techniques
How can you guarantee long-term prevention? Regular inspections and education are key.
| Prevention Tips | Description |
|---|---|
| Travel Precautions | check luggage |
| Shared Item Awareness | avoid sharing |
| Education & Monitoring | stay informed |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I know if I have bed bugs or scabies?
You’ll know if you have bed bugs or scabies by looking for distinct signs: bed bugs leave red welts, while scabies cause intense itching and burrow marks on skin.
How do I know if I have scabies or bed bugs?
You’ll notice distinct signs: scabies causes intense itching, rash, and burrows, while bed bugs leave red welts, often in rows, and are usually found near beds and furniture.
Can you see scabies on bed sheets?
You can’t see scabies on bed sheets because they’re microscopic, but you might notice tiny bumps or burrows on your skin after sleeping, indicating a possible scabies infestation nearby.
What do scabie bites look like?
A red flag for scabies: you’ll spot tiny bumps, blisters, or a rash with intense itching, often in rows, signaling these unwelcome visitors have made themselves at home on your skin.
Do scabies live in mattresses?
You’ll rarely find scabies living in mattresses, as they burrow into human skin, but their eggs or mites can be found in nearby bedding or furniture if infested.
Are scabies more common than bed bugs?
You’ll be shocked, but scabies are incredibly common, affecting millions worldwide, and are often more prevalent than bed bugs in close-contact environments like households and schools.
What are scabies and what do they look like?
You’ll find scabies are microscopic, insect-like parasites that burrow into human skin, causing intense itching and a rash with tiny red bumps and visible burrows, often in skin folds.
What is the difference between bed bugs and scabies mites?
You’ll notice bed bugs are visible, flat, and feed externally, whereas scabies mites are microscopic, burrow under skin, and cause intense itching, distinguishing them substantially.
Are bed bugs harder to get rid of than scabies?
You’ll likely find that bed bugs are harder to get rid of than scabies due to their ability to survive months without feeding and requiring professional pest control.
Do bed bugs bite scabies?
You won’t find bed bugs biting scabies, as bed bugs feed on human blood, not mites, and scabies are microscopic parasites that burrow into human skin, not insects.
Conclusion
Now you can identify the difference between scabies vs bed bugs, taking control of your infestation.
You’ll choose the right treatment, whether it’s topical medications or heat treatment, and reclaim your comfort.
Understanding scabies vs bed bugs is key to relief, so use this knowledge to tackle your issue and find peace.