This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.
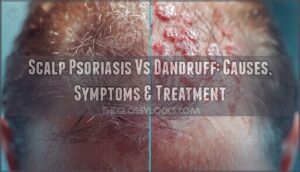
That persistent white flake on your shoulder could signal two entirely different scalp conditions. Up to 50% of adults worldwide deal with dandruff at some point, while 2-3% live with scalp psoriasis—yet these conditions are routinely confused because they both produce flaking and itching.
The distinction matters more than you might think. Dandruff responds well to drugstore shampoos and clears within weeks, but psoriasis requires prescription treatments and long-term management strategies. Misidentifying your condition means wasting time on ineffective remedies while symptoms worsen.
Understanding the key differences between scalp psoriasis and dandruff helps you choose the right treatment approach and know when to seek professional help.
Table Of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Dandruff affects up to 50% of adults and responds to over-the-counter antifungal shampoos within 2-6 weeks, while scalp psoriasis impacts only 2-3% of the population and requires prescription treatments with 4-8 week response times.
- Scalp psoriasis produces thick, silvery-white scales on raised red patches that extend beyond the hairline, whereas dandruff creates fine, white or yellowish flakes that stay confined to the scalp with minimal inflammation.
- Psoriasis stems from autoimmune dysfunction where dysregulated T cells attack healthy skin cells, while dandruff results from Malassezia yeast feeding on scalp sebum and producing irritating fatty acids.
- Persistent symptoms lasting beyond 4-6 weeks of self-treatment, thick plaques spreading past the hairline, or severe itching that disrupts sleep require dermatologist evaluation for accurate diagnosis and prescription intervention.
Scalp Psoriasis Vs Dandruff: Key Differences
Scalp psoriasis and dandruff can look similar at first glance, but they’re fundamentally different conditions. Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease, while dandruff is a common scalp irritation caused by yeast and oil buildup.
Understanding these core differences helps you recognize what’s happening on your scalp and choose the right treatment approach.
Overview of Each Condition
Understanding scalp health starts with knowing the difference between two common scalp conditions. Dandruff refers to mild, chronic flaking caused by Malassezia yeast activity and increased sebum. Scalp psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease marked by well-defined, red, scaly plaques.
Here’s how these conditions compare:
| Feature | Dandruff | Scalp Psoriasis |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Mild flaking condition | Chronic inflammatory disease |
| Cause | Yeast and sebum | Autoimmune activation |
| Scale Type | Fine, diffuse flakes | Thick, silvery patches |
How They Affect The Scalp
Both conditions alter scalp health, but their effects differ. Dandruff causes fine flakes and mild scalp irritation without deep inflammation. Psoriasis symptoms include thick, silvery scales that extend beyond the hairline. Flake removal proves easier with dandruff, while psoriatic plaques require gentle exfoliation. Hair loss can occur when scratching damages follicles. Itch management becomes more challenging with psoriasis due to persistent inflammation affecting scalp care routines. Both conditions benefit from targeted scalp care approaches that address their distinct symptoms and underlying causes.
| Feature | Dandruff | Scalp Psoriasis |
|---|---|---|
| Scale Texture | Fine, waxy flakes | Thick, silvery patches |
| Distribution | Diffuse across scalp | Well-defined plaques at hairline |
| Inflammation | Minimal redness | Intense, uniform redness |
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Dandruff and scalp psoriasis are common scalp conditions with distinct characteristics. Dandruff affects up to 50% of adults globally, while psoriasis impacts 2–3% of the population, with half experiencing scalp involvement. Men show higher dandruff rates due to increased sebum production. Scalp psoriasis usually emerges between ages 15 and 35. Genetic predisposition drives autoimmune disease risk in psoriasis. Both conditions share triggers like stress and climate changes affecting scalp health. Researchers use methodological rigor to study the differences between these conditions.
| Risk Factor | Dandruff | Scalp Psoriasis |
|---|---|---|
| Prevalence | Up to 50% of adults | 2–3% global population |
| Peak Age | Adolescence to young adulthood | Ages 15–35 |
| Gender Trend | Higher in males | Similar across genders |
Causes of Scalp Psoriasis and Dandruff
Understanding what causes these two conditions is the first step toward effective treatment. Psoriasis and dandruff stem from completely different biological processes in your body. If you’re dealing with those stubborn plaques, exploring natural remedies for scalp psoriasis can help you find gentle relief without harsh chemicals.
The following sections break down the specific triggers and mechanisms behind each condition. Choosing the right anti-dandruff shampoo can help address these underlying causes while soothing your scalp.
Autoimmune Triggers in Psoriasis
Psoriasis stems from an autoimmune disease where your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This autoimmune disorder involves dysregulated T cells that trigger an inflammatory response through cellular signaling pathways.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease where your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, triggering inflammation through dysregulated T cells
Genetic predisposition interacts with environmental factors like stress and infections to activate these immune pathways. The resulting cascade of cytokines drives rapid skin cell turnover, creating the characteristic psoriatic plaques that can lead to psoriatic arthritis in some cases.
Understanding the language patterns of medical terminology can help clarify the intricacies of autoimmune diseases.
Yeast and Sebum in Dandruff
Unlike psoriasis, dandruff arises when Malassezia yeast feeds on scalp sebum and produces irritating fatty acids. This fungal activity triggers flaking and itching, especially in oily scalps where sebum regulation falters.
Seborrheic dermatitis represents a more severe form involving the same yeast-sebum interaction. Distinguishing between these conditions often requires professional seborrheic dermatitis evaluation and treatment to ensure proper management.
You’ll find relief through dandruff treatment targeting both the yeast infection and excess oil. Antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole or zinc pyrithione restore scalp health by controlling Malassezia overgrowth.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Your family tree plays a key role in scalp psoriasis risk, with immune-related gene variants increasing susceptibility through polygenic mechanisms. Environmental triggers like stress, smoking, and obesity interact with this genetic predisposition to spark flares.
Epigenetic factors and microbiome shifts further modulate autoimmune disease management. Effective immune system health requires addressing both inherited vulnerabilities and modifiable lifestyle exposures that heighten inflammation.
Symptoms: How to Tell Them Apart
You can’t always tell the difference between scalp psoriasis and dandruff just by looking at flakes on your shoulders. Both conditions need different approaches, so if you’re dealing with persistent flakes or irritation, exploring scalp exfoliation techniques for dandruff control can help you figure out what’s actually going on.
The two conditions create distinct patterns on your scalp that become clear once you know what to look for.
Here’s how to recognize which condition you’re dealing with based on appearance, sensation, and location.
Flaking, Scaling, and Patch Differences
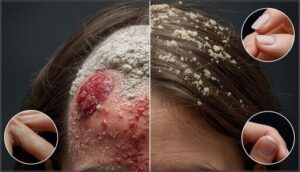
The texture and appearance of scales tell a different story with each condition. Dandruff produces fine, white or yellowish flakes that shed easily when you brush your hair.
Scalp psoriasis creates thicker, silvery-white scales on raised red patches with sharp borders. These scaly patches stick more firmly to your scalp and often extend beyond your hairline.
Flaking severity is clearly milder with dandruff, while psoriasis forms persistent plaques that resist gentle removal.
Itching and Redness Comparison
Itch intensity and redness patterns reveal critical clues about your scalp condition. Scalp psoriasis triggers persistent itchiness in 60-90% of patients, often with burning sensations and bright red patches that have well-defined borders.
Dandruff causes milder, intermittent itchy scalp symptoms in 20-40% of cases, with diffuse redness or none at all.
Your scalp irritation from psoriasis worsens with heat, while dandruff itchiness often decreases with regular washing.
Areas Affected on The Scalp and Beyond
Scalp psoriasis often reaches beyond your hairline, creating thick, silvery plaques on your forehead, neck, and behind your ears. These skin lesions form well-defined borders with notable scalp inflammation.
Dandruff usually stays confined to your scalp, producing finer, yellowish flakes with less facial symptoms.
Psoriasis symptoms may include nail changes or joint pain, while dandruff rarely affects areas beyond an itchy scalp with mild neck irritation.
Diagnosis: Identifying Your Scalp Condition
You can often identify dandruff or psoriasis by examining your scalp at home.
A dermatologist provides the most accurate diagnosis when symptoms persist or worsen. Your doctor may use clinical observation or specific tests to distinguish between these conditions.
Clinical Signs and Self-Assessment
You can identify your condition at home with a careful scalp examination. Look for well-defined red plaques with thick, silvery scales that extend beyond your hairline—that’s scalp psoriasis. Dandruff shows loose, white or yellowish flakes without clear borders.
Note your itch patterns and redness levels. Psoriasis symptoms include persistent itching and bleeding when you remove scales. A flaky scalp with milder itching suggests dandruff. Skin biopsy and flake analysis confirm uncertain cases.
When to See a Dermatologist
Your self-assessment helps, but persistent symptoms demand specialist consultation. See a dermatologist when over-the-counter treatments fail after four to six weeks or when thick, silvery plaques spread beyond your hairline.
Severe itching relief methods often require prescription-strength options. If burning or pain disrupts your sleep, you need a scalp symptom evaluation.
A dermatologist referral ensures accurate diagnosis between scalp psoriasis and dandruff through targeted examination and, when necessary, skin testing for severe case management.
Diagnostic Tools and Tests
Your dermatologist relies on dermoscopy analysis to magnify scalp lesions and reveal subtle differences between psoriasis and dandruff. Trichoscopy findings identify punctate scaling patterns that distinguish these dermatological conditions.
When skin inflammation proves ambiguous, a skin biopsy confirms psoriasis through histopathology. Patch testing excludes contact dermatitis as a contributing factor.
Clinical scoring systems quantify the severity of scalp conditions, guiding your treatment plan with measurable precision rather than guesswork.
Treatment Options for Each Condition
Treatment approaches differ markedly between dandruff and scalp psoriasis. Dandruff usually responds well to over-the-counter shampoos, while psoriasis often requires prescription medications and more intensive management.
Understanding your options helps you find the right treatment for your specific scalp condition.
Over-the-Counter Dandruff Solutions
For most cases of dandruff, medicated shampoo offers effective relief without prescription. You’ll find products containing zinc pyrithione, ketoconazole, or selenium sulfide at your local pharmacy. These ingredients target Malassezia yeast and reduce flaking.
Apply the shampoo to your scalp, massage gently for 3–5 minutes, then rinse. Use 2–3 times weekly initially. If symptoms persist after 4–6 weeks, consult a dermatologist for stronger dandruff treatment options.
Prescription Treatments for Psoriasis
When over-the-counter medicated shampoo doesn’t control your scalp psoriasis, prescription treatments become necessary. Topical corticosteroids reduce inflammation and are often paired with vitamin D analogs like calcipotriene in combination treatments.
For moderate to severe cases, systemic medications—including methotrexate or apremilast—may be prescribed. Biologic therapy targets specific immune pathways and offers relief when other options fail.
Phototherapy options, particularly narrowband UVB, can improve stubborn plaques under medical supervision.
Home Care and Lifestyle Tips
Beyond medications, daily habits shape scalp health. Gentle shampooing two to three times weekly with warm water prevents irritation for both scalp psoriasis and dandruff. Scalp massage with fingertips loosens flakes without trauma.
Stress reduction through mindfulness and regular sleep improves skin barrier recovery.
A healthy diet rich in omega-3s and adequate hydration supports overall skin health. These hair care tips complement medical treatments effectively.
Managing Flare-Ups and Preventing Recurrence
Both dandruff and psoriasis respond better when you stay ahead of flare-ups rather than just reacting to them. A proactive approach helps keep symptoms in check and reduces the frequency of outbreaks.
The following strategies focus on daily routines, identifying your personal triggers, and building sustainable habits for long-term scalp health.
Scalp Care Routines
You can manage both scalp psoriasis and dandruff with a consistent skin care routine. Daily cleansing with medicated shampoos reduces flaking. Gentle combing prevents scalp trauma.
Scalp exfoliation removes buildup when used sparingly. Hair oiling and scalp massage improve hydration without heavy residue. A scalp treatment plan should include fragrance-free products.
Your scalp care approach depends on whether you have psoriasis or simple dandruff.
Triggers to Avoid
You can prevent flare-ups by steering clear of harsh chemicals in shampoos and hair dyes. Environmental factors like cold, dry air often worsen both scalp psoriasis and dandruff. Tight headwear increases friction on vulnerable skin.
Lifestyle triggers include stress, which amplifies inflammation. Stress management techniques reduce autoimmune activity.
Dietary influences matter—excess alcohol and high-sugar foods can aggravate symptoms. Identifying your specific triggers protects scalp health and minimizes the need for flaky scalp solutions.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Consistent scalp maintenance and treatment adherence form the backbone of chronic condition management. You’ll benefit from symptom tracking to identify flare patterns and adjust your approach. Lifestyle modifications—stress reduction, balanced nutrition, adequate sleep—support autoimmune disease treatment over time.
Preventive measures include rotating prescribed topicals with gentle moisturizers. For managing scalp conditions like scalp psoriasis, schedule regular dermatology follow-ups. Scalp psoriasis treatment requires patience and persistence, not quick fixes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can stress worsen scalp psoriasis or dandruff?
Yes, stress can worsen both conditions. It triggers inflammation in scalp psoriasis and alters sebum production in dandruff, amplifying itch and flaking.
Managing stress promotes better scalp health alongside targeted treatments.
Are there specific dietary changes that help?
While omega-3s and probiotics show promise for inflammatory skin conditions, evidence remains mixed for scalp psoriasis and dandruff.
Focus on vitamin D correction if deficient, adequate hydration, and limiting high-sugar foods for overall scalp health.
Can children develop scalp psoriasis or dandruff?
Children can develop both scalp psoriasis and dandruff. About 1–2% of children have pediatric scalp psoriasis, while dandruff affects up to 40–50% of adolescents, particularly after puberty begins.
How long does treatment take to work?
Patience pays off when treating scalp conditions. Dandruff symptoms often improve within 2 to 6 weeks using medicated shampoos.
Scalp psoriasis treatment usually requires 4 to 8 weeks for visible healing, though severe cases may need longer response times.
Can scalp psoriasis lead to hair loss?
Scalp psoriasis can cause temporary hair loss through inflammation and scratching. Telogen effluvium and traction alopecia may occur during flares. Scarring is rare.
Treating scalp inflammation with corticosteroids helps restore hair regrowth.
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between scalp psoriasis vs dandruff changes everything about your treatment timeline. Dandruff resolves with targeted shampoos within weeks. Psoriasis requires prescription interventions and sustained management.
Your scalp’s persistent flaking deserves accurate identification rather than guesswork. Start with over-the-counter treatments for two weeks. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a dermatologist for a definitive diagnosis.
The right approach eliminates months of frustration and prevents unnecessary progression of treatable conditions.
- https://www.psoriasis.org/about-psoriasis
- https://www.aad.org/public/everyday-care/hair-scalp-care/scalp/treat-dandruff
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22828-scalp-psoriasis
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dandruff/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353854
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531463/