This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.
Your scalp itches, but it’s not just the usual dry skin. The itch persists, and you notice small patches where your hair looks thinner, maybe even broken off near the roots. You might see flaky skin or a strange redness that won’t respond to your regular shampoo.
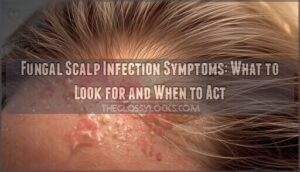
These signs often point to a fungal scalp infection, a condition that affects millions but frequently goes misdiagnosed as dandruff or dermatitis. Fungal scalp infection symptoms range from mild itching to severe inflammation with permanent hair loss if left untreated. The fungi invade hair follicles and damaged skin, creating distinct patterns that trained eyes can recognize.
Catching these symptoms early makes treatment more effective and prevents spread to others or other areas of your body.
Table Of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Fungal scalp infections, primarily tinea capitis from dermatophytes or Candida yeast, cause distinct symptoms including persistent itching, ring-shaped scaly patches, hair breakage at follicles creating “black dots,” and inflammation that can lead to permanent hair loss if untreated.
- Early recognition matters because symptoms progress from mild itching to severe follicle damage over days to weeks, with children typically showing more inflammatory patchy hair loss while adults experience subtler diffuse thinning that can mask infection severity.
- Accurate diagnosis requires clinical examination for characteristic patterns like broken hairs and scaling, often confirmed by lab tests such as fungal culture or PCR, especially when visual inspection or initial self-treatment fails after four weeks.
- Effective management combines early intervention with antifungal shampoos or oral medications, strict hygiene to prevent spread through shared items, and gentle post-treatment scalp care using fragrance-free products to support barrier repair and hair regrowth within three to six months.
What is a Fungal Scalp Infection?
A fungal scalp infection happens when fungi invade your scalp’s hair follicles or damaged skin. These infections range from mild irritation to severe inflammation that causes permanent hair loss.
Understanding what these infections are, which types affect your scalp, and how they develop helps you recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate treatment.
One telltale sign of an unhealthy scalp is persistent itching, which often accompanies these infections and shouldn’t be ignored.
Definition and Overview
A scalp fungal infection is a superficial mycosis where fungi invade your scalp’s outer layers and hair shafts. Dermatophyte infection, particularly tinea capitis, accounts for most cases through keratin invasion of follicles and skin.
Identifying what causes poor scalp health early helps you distinguish fungal infections from other inflammatory conditions affecting the scalp.
Scalp yeast infection involves Candida species disrupting your scalp’s fungal ecology. This scalp infection remains confined to surface structures in healthy individuals, though fungal pathogenesis varies by organism and your body’s response.
Understanding fungal infection types is vital for effective treatment and prevention.
Common Types Affecting The Scalp
Tinea capitis, or ringworm of the scalp, remains the most frequent fungal scalp infection you’ll encounter. Microsporum and Trichophyton dermatophyte types invade your hair shafts and follicles, creating distinct infection patterns.
You might also develop a scalp yeast infection from Candida species, particularly if your immune system is compromised. Malassezia can disrupt your scalp ecosystem with seborrheic dermatitis, though it differs from true dermatophyte infections.
Each fungal species requires specific treatment options for effective resolution. Researchers rely on scientific study audits to verify the accuracy of their findings.
How Fungal Infections Develop
Your infection starts when fungal spores land on your scalp and bind to keratin through dermatophyte adhesion. These organisms thrive in warm, moist conditions and begin scalp colonization by secreting enzymes that break down your hair’s protective barriers.
Keratin invasion follows distinct patterns:
Fortunately, effective hair loss remedies for women can help restore growth once the underlying fungal infection is properly treated.
- Fungal spore transmission occurs through direct contact, shared combs, or infected animals
- Scalp yeast infection from Candida develops when moisture disrupts your skin’s natural balance
- Fungal growth patterns vary—some species grow inside hair shafts, others coat the exterior
- Scalp fungal infection progresses over days to weeks as organisms penetrate deeper follicular structures
Key Symptoms of Fungal Scalp Infection
Recognizing fungal scalp infections early makes treatment more effective and prevents complications. The symptoms vary from person to person, but certain patterns appear consistently across different types of infections.
Itching, flaking, and tenderness often signal underlying scalp inflammation that requires targeted treatment to restore scalp health.
You’ll want to watch for these key signs that indicate fungi have taken hold on your scalp.
Itching and Scalp Discomfort
Itching is often the first signal that something’s wrong—your scalp may feel persistently uncomfortable, especially at night or after sweating.
This itch differs from dandruff; it’s localized to specific patches where the fungal infection is active, creating ring-shaped patterns or circular areas of discomfort.
These infections require antifungal treatment to clear the scalp condition and prevent permanent hair loss.
Scratching brings temporary relief but worsens irritation, potentially inviting bacterial complications that prolong your recovery.
Redness, Swelling, and Inflammation
Visible changes often follow itching—red or purple patches signal an inflammatory response as your immune system confronts the fungal infection. Scalp erythema with swelling appears in roughly 20–60% of ringworm cases, especially in children, and these fungal infection signs may worsen before treatment begins.
Inflammation mechanisms involve:
- Immune cells releasing cytokines that trigger redness and warmth
- Edema around hair follicles, creating tender, raised areas
- Secondary bacterial colonization if scratching breaks the skin
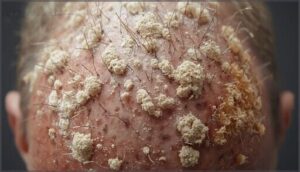
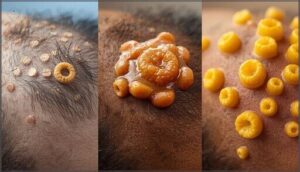
Flaky or Scaly Patches
White or yellow scales cluster where fungi disrupt your skin’s natural renewal cycle, creating Scalp Flake Causes you’ll notice on clothing or pillows. These flaky scales vary from dry powder to greasy patches depending on the organism—Scalp Yeast Infection often produces thicker, oilier buildup.
Scaly patches around affected follicles confirm follicular involvement, making Fungal Scale Treatment essential before permanent damage occurs.
Hair Loss and Broken Hairs
Patches of hair loss reveal where fungal invasion weakens follicles, causing strands to snap close to the scalp surface. You’ll spot stubby ends or irregular breaks scattered across itchy scalp areas—telogen effluvium accelerates shedding while inflammation disrupts moisture balance, making hair breakage worse than scalp damage alone would cause.
Fungal invasion weakens follicles, causing hair to snap near the scalp while inflammation and shedding worsen the breakage
- Weakened shafts break near roots from follicle inflammation and moisture imbalance
- Scratching accelerates mechanical breakage beyond what the fungal infection directly causes
- Premature shedding occurs as telogen effluvium compounds scalp health decline
- Follicle repair depends on early treatment to restore hair regrowth and prevent permanent loss
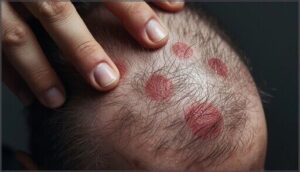
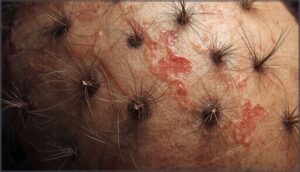
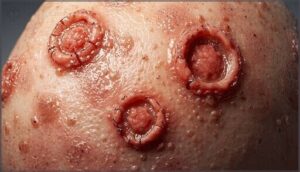
Ring-Shaped Lesions and Black Dots
Circular patches with raised, scaly borders mark tinea capitis territory on your scalp, revealing dermatophyte infections at work. Black dots appear where broken hair shafts snap at follicle openings—a hallmark of ringworm symptoms you can’t miss during examination.
These scalp infection patterns distinguish fungal lesion types from non-fungal conditions.
| Feature | What You’ll Notice |
|---|---|
| Ring shape | Active, scaling border with central clearing |
| Black dots | Broken hairs at scalp surface from fungal invasion |
| Distribution | Scattered or clustered patches across affected areas |
| Texture | Rough, flaky edges surrounding itchy scalp zones |
How Fungal Scalp Infection Symptoms Differ
Not all scalp infections look or behave the same way. Fungal infections present differently depending on the organism involved, the person’s age, and whether bacteria have joined the picture.
Understanding these differences helps you recognize what you’re dealing with and when to seek treatment.
Fungal Vs. Bacterial Scalp Symptoms
When you’re trying to tell fungal infections apart from bacterial symptoms on your scalp, look at the lesions themselves. Fungal signs like ringworm of the scalp often show ring-shaped patterns with scaling and broken hairs, while bacterial symptoms tend to produce tender, crusty areas with pus.
Diagnostic tools like skin cultures help distinguish these infection types when your itchy scalp needs clarity.
Yeast (Candida) Vs. Ringworm (Tinea Capitis)
Your scalp can host two very different fungal infection types, and telling them apart matters for effective treatment. Candida yeast infections create diffuse greasy scaling without the circular patches or broken hairs you’d see with ringworm (tinea capitis). Here’s what sets them apart:
- Tinea capitis forms ring-shaped lesions with black dot hair breakage at the scalp surface
- Candida produces generalized greasy scales, often linked to immune issues or antibiotic use
- Ringworm transmission happens child-to-child through shared combs, while yeast overgrowth stems from your body’s own flora
Understanding these differences guides proper scalp yeast treatment and candida prevention strategies.
Symptoms in Children Vs. Adults
Age-related symptoms reveal striking fungal infection patterns you shouldn’t overlook. Children with ringworm of the scalp show patchy hair loss with black-dot breakage and intense scalp itch variations—often worse at night—while adults experience subtler diffuse thinning with milder inflammation.
Child health issues include more inflammatory crusted lesions, whereas yeast infection symptoms in adults may present as persistent flaking with minimal redness, potentially masking infection severity.
Diagnosing Fungal Scalp Infections
Getting the right diagnosis is the first step toward clearing up a fungal scalp infection. Your doctor will examine your scalp closely, looking for telltale signs like scaling, broken hairs, and inflammation patterns.
In many cases, lab tests confirm what type of fungus you’re dealing with so treatment can target it directly.
Clinical Examination and Symptom Recognition
Your doctor begins with a careful scalp inspection, looking for telltale signs of fungal infections like broken hairs, scaly patches, or inflammation. Ringworm of the scalp often reveals characteristic patterns during this clinical diagnosis:
- Black dots where hairs snap off at the surface
- Gray patches with dull, broken hair shafts
- Pustules or crusting suggesting inflammatory infection
- Comma-shaped hairs visible during dermoscopic exam
Hair analysis and specialized tools like Wood’s lamp complete the fungal testing process, though some scalp fungal infection cases need deeper investigation.
Laboratory Tests (Cultures, PCR)
When a visual exam doesn’t tell the whole story, your doctor orders laboratory work to confirm dermatophyte testing. Fungal culture on special agar identifies the exact species causing your scalp infection, though results take up to four weeks.
PCR assays deliver faster molecular diagnosis—often within days—detecting fungal infections with high accuracy from plucked hairs or scales, helping you start targeted treatment sooner.
When to Seek Professional Help
After lab results confirm your scalp infection, knowing when professional help becomes urgent matters. Seek medical evaluation immediately if you develop fever above 104°F, notice pus-filled lesions draining yellow fluid, or see rapid spread across multiple scalp areas.
Treatment failure after four weeks of self-care, underlying conditions like diabetes or HIV, and severe infections demand dermatological assessment to prevent complications.
Managing and Preventing Scalp Fungal Symptoms
Once you’ve confirmed a fungal scalp infection, your focus shifts to treatment and prevention. Managing symptoms early helps limit damage and speeds recovery, while taking the right steps can prevent the infection from spreading or coming back.
The following sections cover how to address symptoms promptly, reduce transmission risk, and support your scalp as it heals.
Early Symptom Management
When you notice that itchy rash, cool compresses applied two to three times daily provide itch relief and reduce discomfort. Keep your nails short to avoid scratching, which worsens scalp infections.
Use non-prescription antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole or selenium sulfide to address the fungal infection early. Gentle scalp care with mild products promotes scalp health during symptom tracking and fungal prevention efforts.
Preventing Spread and Recurrence
Consistent hygiene practices reduce recurrence risk and prevent scalp infection spread to others. Infection control requires diligence with these prevention methods:
- Wash your hands thoroughly after touching your scalp, and don’t share combs, brushes, or hats with others
- Complete your full antifungal therapy course—even when symptoms disappear—to eliminate fungal infections completely
- Launder bedding and clothing in hot water to maintain scalp health and prevent infectious diseases
Supporting Scalp Health During Recovery
Your scalp barrier needs active repair after fungal infections clear. Switch to fragrance-free, sulfate-free products and wash just two to three times weekly with lukewarm water. This protects natural oils and speeds hair regrowth. Add aloe vera or ceramide-based treatments to rebuild your scalp’s defense system and reduce post-infection care complications.
| Post-Infection Care Step | How It Assists Scalp Health |
|---|---|
| Use antifungal shampoos intermittently | Prevents fungal resistance and reinfection |
| Apply barrier-repair formulations | Restores lipid levels and scalp barrier integrity |
| Avoid tight hairstyles and chemicals | Reduces traction damage during hair regrowth |
| Disinfect combs and pillowcases | Lowers re-exposure risk and maintains scalp hygiene |
| Follow up with dermatology | Monitors recovery and manages persistent skin health issues |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can fungal scalp infections cause permanent scarring?
Yes, though uncommon. Severe inflammation from kerion or untreated scalp ringworm can destroy follicles permanently.
Early treatment reduces scarring risk factors by limiting follicle damage before fibrosis locks in hair loss.
Are fungal scalp infections contagious through swimming pools?
You can’t catch a scalp infection directly from pool water, but dermatophyte fungi survive in chlorinated pools.
The real contagion risk comes from shared towels, locker room floors, and communal showers around swimming areas.
How long does complete hair regrowth take?
After effective treatment, your hair usually regrows within three to six months.
However, scalp healing and follicle recovery depend on infection severity, treatment adherence, and individual regrowth factors influencing post-infection care timelines.
Do antifungal shampoos work without oral medication?
Think of a garden gate: sometimes the barrier alone keeps intruders out.
Antifungal shampoos can clear mild scalp infections without oral medication, though widespread fungal disease or resistant cases need systemic antifungal treatment for complete scalp health restoration.
Conclusion
Think of your scalp as a garden—left unattended, unwanted visitors thrive. Recognizing fungal scalp infection symptoms early gives you the tools to restore balance before permanent damage takes root.
Persistent itching, unusual flaking, or patchy hair loss aren’t minor annoyances to dismiss. They’re your body’s clear signals that intervention is needed.
Act when symptoms appear, consult a dermatologist for accurate diagnosis, and follow treatment protocols completely. Your scalp’s health depends on your willingness to respond decisively.
- https://links.e.response.mayoclinic.org/EmailPreview-GeneralHealth
- https://mcforms.mayo.edu/mc5200-mc5299/mc5256-01.pdf
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1091351-overview
- https://medicinetoday.com.au/mt/2020/july/supplements/feature-article/overview-cutaneous-fungal-infections
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22967-scalp-yeast-infection