This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.

When you shave against the grain or use dull blades, you’re basically setting up a perfect storm for trouble.
Dead skin cells clog your follicles, trapping newly cut hairs beneath the surface.
If you’ve got curly or coarse hair, you’re even more prone to this frustrating cycle.
Think of it like trying to thread a needle backward – your hair gets confused about which direction to grow.
The good news is that simple adjustments to your routine can break this cycle completely, and with the right approach, you can avoid this trouble and have healthier skin, which is the ultimate good news.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Shaving Causes Ingrown Hair
- Ingrown Hair Risk Factors
- Symptoms of Ingrown Hairs
- Preventing Ingrown Hairs
- Medical Treatments for Ingrown Hairs
- Managing Ingrown Hair Complications
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can a shave cause ingrown hair?
- What are ingrown hairs?
- Can shaving & tweezing cause ingrown hairs?
- What are ingrown hairs & razor bumps?
- What causes ingrown hairs on the face?
- How to prevent ingrown hairs?
- How do I stop ingrown hairs after shaving?
- Why am I suddenly getting more ingrown hairs?
- What is the fastest way to heal an ingrown hair?
- What causes ingrown hairs if you don’t shave?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- You’re creating sharp-angled hair tips when you shave that act like tiny spears, easily piercing back into your skin as they regrow, especially when you shave against the grain or use dull blades.
- You’re at higher risk for ingrown hairs if you have curly or coarse hair, African ancestry, or shave daily – with up to 80% of Black men experiencing razor bumps due to genetic hair structure.
- You can prevent most ingrown hairs by exfoliating 2-3 times weekly, using sharp razors, shaving with warm water in the direction of hair growth, and wearing loose clothing after shaving.
- You’ll recognize ingrown hairs by raised red bumps, itching, and pus-filled sores that can lead to serious complications like bacterial infections, permanent scarring, and dark spots if you don’t treat them properly.
Shaving Causes Ingrown Hair
When you shave, you’re cutting hair at a sharp angle that creates pointed tips, which can easily pierce back into your skin as they grow.
Sharp-angled hair tips from shaving act like tiny spears, piercing back through your skin as they regrow.
This happens because shaving removes hair below the skin’s surface, especially when you shave against the grain or apply too much pressure with your razor, leading to pointed tips that can cause discomfort.
Hair Growth Patterns
When you shave, you’re working against your body’s natural hair growth patterns.
Your hair doesn’t grow straight up like you might think.
Instead, each follicle has its own unique hair direction and growth speed influenced by your hair cycle and hormonal influence.
Understanding these follicle shape variations helps explain why shaving ingrown hairs develop when hair growth direction gets disrupted by your razor.
Curly Hair Texture
Curly hair texture creates a perfect storm for ingrown hairs.
Your curl patterns naturally bend hair back toward the skin after shaving, while follicle shape influences how hair exits.
Hair elasticity and porosity affect product absorption, making proper preparation essential.
This texture increases pseudofolliculitis barbae risk because curved hairs easily pierce skin surfaces once cut, leading to a higher risk of ingrown hairs.
Dead Skin Clogging Follicles
Dead skin cells naturally shed from your body every day, but they don’t always fall away cleanly.
When these cells accumulate around your hair follicle, they create a blockage that traps growing hair beneath the surface.
This skin buildup forces hair to grow sideways or curl back into itself, causing painful ingrown hair bumps after shaving.
Razor Bump Formation
When your razor cuts hair at sharp angles, those pointed tips become tiny spears that pierce back into your skin.
This creates razor bumps – those angry red welts that burn and itch after shaving.
Here’s how blade mechanics trigger shave bumps:
- Shaving Angle determines how sharp hair tips become after cutting
- Blade Sharpness affects clean cuts versus jagged, piercing ends
- Skin Hydration softens follicles to prevent follicle damage
- Pressure Applied controls how deep cuts penetrate, causing shaving irritation
Ingrown Hair Risk Factors
Your genetics and hair characteristics play a major role in determining how likely you’re to develop ingrown hairs after shaving.
Understanding these risk factors can help you adjust your shaving routine to prevent painful razor bumps before they start, which involves recognizing the importance of prevention in your daily shaving habits.
African Ancestry
Unfortunately, men of African ancestry face an 80% higher risk of developing pseudofolliculitis barbae after shaving.
Unfortunately, 8 out of 10 Black men develop razor bumps after shaving due to genetic hair structure.
Your genetic predisposition creates unique hair morphology challenges that standard grooming practices don’t address.
Cultural practices often emphasize clean-shaven appearances, yet treatment disparities limit dermatological access for skin of color concerns.
| Challenge | Impact on African Ancestry |
|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | 80% of Black men experience razor bumps |
| Treatment Disparities | Limited specialized dermatological access |
| Cultural Expectations | Pressure for clean-shaven professional appearance |
Curly or Coarse Hair
Your hair’s natural texture plays a major role in ingrown hair causes.
Curly hair naturally curves back toward your skin after shaving, making it more likely to pierce through and grow inward.
Coarse hair management becomes trickier because thick strands create sharper points when cut.
Hair curl genetics mean some people face higher ingrown hair severity, especially with ethnic hair differences affecting hair follicle shape.
Hair Thickness
Your hair thickness plays a bigger role in ingrown hair causes than you might think.
Thick, coarse hair acts like a tiny spear that easily pierces back into your skin after shaving.
Here’s how hair density impacts your shaving experience:
- Coarse Hair Problems – Thick strands create sharper points when cut
- Fine Hair Issues – Thin hair bends easier, reducing penetration risk
- Thickness and Ingrowns – Dense follicles trap hair more frequently
Understanding what is hair density is essential for proper hair care.
Frequent Shaving
Daily shaving habits create a perfect storm for ingrown hairs. Each time you shave, you’re cutting hair at sharp angles that can pierce back into your skin.
Your shaving frequency directly impacts your risk level.
| Shaving Frequency | Risk Level | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | High | Use electric clippers |
| Every 2-3 days | Moderate | Focus on technique matters |
| Weekly | Low | Standard blade quality works |
This information suggests that understanding your shaving frequency is crucial to managing and preventing ingrown hairs.
Symptoms of Ingrown Hairs
You’ll recognize ingrown hairs by their telltale signs, which include raised red bumps, itching, and small pus-filled sores that resemble pimples.
These symptoms often appear in areas you’ve recently shaved, and you might notice darker patches of skin around the affected spots, which can be associated with ingrown hairs.
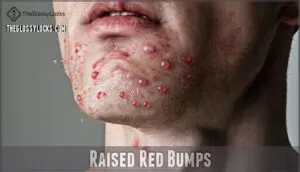
Raised Red Bumps
Those telltale raised red bumps are your skin’s way of waving a red flag.
These razor bumps typically appear as small, pimple-like bumps within hours of shaving.
The initial appearance varies—some start barely visible while others emerge angry and inflamed.
Bump severity often depends on bump location, with sensitive areas like your neck showing more dramatic skin irritation than your legs.
Itching and Discomfort
That persistent scratching sensation isn’t just annoying—it’s your skin’s alarm bell.
Ingrown hair itching occurs when trapped hairs trigger inflammation beneath the surface.
This discomfort ranges from mild irritation to intense burning sensations.
Razor bumps often feel tender to touch, creating ongoing pain management challenges.
Understanding these symptom severity levels helps you recognize when soothing techniques become necessary for effective itch relief.
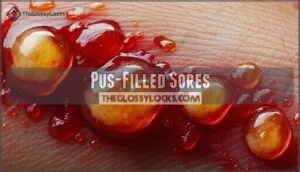
Pus-Filled Sores
When infected ingrown hair bumps develop, they transform into painful pus-filled sores that signal your body’s battle against bacteria.
The pus composition contains white blood cells fighting infection, creating tender boils that throb with each movement.
Without proper sore treatment, infection severity escalates, increasing scarring potential.
Pain management becomes essential as these razor bumps demand immediate attention to prevent complications.
Consider gentle exfoliation methods to prevent future occurrences and reduce the risk of infection.
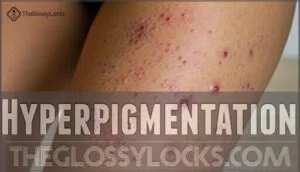
Hyperpigmentation
Beyond infected bumps, ingrown hairs often leave their mark through hyperpigmentation—dark spots that linger long after the initial irritation fades.
This skin discoloration particularly affects people with darker skin tones, creating patches that can take months to fade.
Here are three key hyperpigmentation causes from shaving:
- Inflammatory response triggers excess melanin production
- Repeated irritation from aggressive shaving techniques
- Picking or scratching infected ingrown hair bumps
Preventing Ingrown Hairs
You can prevent most ingrown hairs by changing how you shave and care for your skin before and after hair removal.
Simple steps like using warm water, sharp razors, and regular exfoliation will substantially reduce your risk of developing painful razor bumps, which can be achieved through simple steps.
Exfoliation Techniques
Regular exfoliation removes dead skin cells that trap hair beneath the surface.
Physical scrubs with sugar or salt work well, while chemical exfoliants like glycolic acid dissolve cellular buildup.
Exfoliate 2-3 times weekly before shaving for best ingrown hair prevention.
Post-exfoliation care includes moisturizing immediately to prevent dryness and irritation that could worsen shaving-related skin problems.
Using shaving cream can reduce friction effectively during shaving to achieve smooth results with less irritation and promote healthy skin.
Shaving With Warm Water
Warm water works like magic for your skin before shaving.
The heat opens your pores and softens coarse hair, making it easier to cut cleanly.
This simple step reduces irritation and helps prevent ingrown hairs from forming.
Consider using a warm water razor for enhanced comfort.
Splash warm water on the area for 30 seconds, or shave right after a hot shower for best results.
Using Sharp Razors
Sharp razor blades make all the difference in preventing ingrown hair. Dull blades tug and tear hair instead of cutting cleanly, increasing skin irritation and razor bumps.
Here’s how blade sharpness affects your shaving results:
- Fresh blades cut hair cleanly without yanking or pulling
- Proper razor angle reduces cuts and skin damage
- Replace blades after 5-7 shaves to maintain effectiveness
- Single-blade razors cause less irritation than multi-blade options
Using shaving gel can help with sensitive skin irritation.
Avoiding Tight Clothing
Your fabric choice matters just as much as your razor selection.
Tight clothing traps sweat and friction against freshly shaved skin, creating perfect conditions for ingrown hairs. Loose, breathable fabrics reduce skin irritation and improve circulation around hair follicles.
| Clothing Type | Impact on Skin | Ingrown Hair Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Tight synthetic fabrics | High friction, poor airflow | Very High |
| Loose cotton clothing | Good breathability, minimal rubbing | Low |
| Compression garments | Restricted circulation, constant pressure | High |
| Moisture-wicking materials | Keeps skin dry, reduces bacteria | Medium |
| Silk or bamboo fabrics | Smooth texture, natural cooling | Very Low |
Choose clothing alternatives that prioritize post-shave comfort over style.
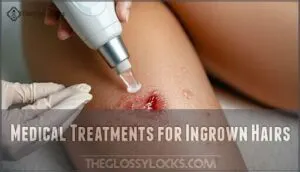
Medical Treatments for Ingrown Hairs
When home remedies aren’t enough to treat your stubborn ingrown hairs, medical treatments can provide the relief you need.
Your doctor can prescribe antibiotic ointments for infections, steroid creams to reduce inflammation, or recommend laser hair removal and electrolysis for long-term prevention.
Antibiotic Ointments
When ingrown hair becomes infected, antibiotic ointment offers targeted relief.
Apply topical antibiotics like bacitracin or mupirocin directly to infected bumps twice daily.
Watch for side effects including skin irritation or redness.
You can find various related products online.
Preventative use isn’t recommended due to resistance concerns.
Consider alternative antibiotics if initial treatment fails.
Always clean the area before ointment application for maximum effectiveness.
Steroid Creams
Steroid creams tackle inflammation from shaving-related bumps when antibiotics aren’t enough.
These topical treatments reduce redness and calm irritated skin through different potency levels and application methods.
Consider these steroid cream essentials:
- Low-potency options work best for facial skin care
- Medium-strength formulas target body ingrown hairs effectively
- Side effects include skin thinning with long-term use
- Application methods require thin, gentle coverage twice daily
- Alternative options exist if steroids cause skin irritation
Electrolysis
Electrolysis technology delivers a mild electrical zap directly into hair follicles, ensuring permanent hair loss.
This hair removal method requires multiple sessions, making treatment duration longer than other options.
Electrolysis efficacy remains unmatched for preventing ingrown hairs permanently. Potential side-effects include temporary redness and swelling.
Electrolysis cost varies by treatment area size and session frequency.
Laser Hair Removal
Concentrated light beams make laser hair removal your strongest weapon against stubborn ingrown hairs.
This treatment targets hair follicles’ pigment, destroying them at the root. It’s especially effective for dark hair and works best on lighter skin types.
Laser hair removal can also reduce ingrown hairs by targeting the hair follicle.
Key considerations for laser treatment:
- Laser efficacy reaches 90% hair reduction after completing your full treatment series
- Treatment cost varies widely but saves money compared to lifetime shaving expenses
- Potential risks include temporary redness and sensitivity, though maintenance needed remains minimal
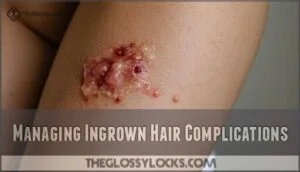
Managing Ingrown Hair Complications
When ingrown hairs aren’t treated properly, you’ll face serious complications like bacterial infections, permanent scarring, and dark spots that can last for months.
You need to recognize these warning signs early and take immediate action to prevent long-term skin damage that affects your appearance and comfort.
Infections and Scarring
When you ignore infected ingrown hairs, you’re playing with fire.
Bacterial infections can spread beyond the initial bump, creating painful pus-filled sores that require antibiotic treatment.
Staph infection becomes a real threat if bacteria enters deeper skin layers.
Picking at bumps often leads to permanent scar tissue formation, while severe cases may develop keloid scars or pilonidal cysts.
Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation
After infections clear up, you might notice dark spots where your ingrown hair bumps used to be.
This hyperpigmentation happens because inflammation triggers extra melanin production, especially in skin of color.
PIH severity depends on how deep the inflammation went, and PIH duration can last months, but PIH treatments like hydroquinone cream help fade these stubborn dark spots faster than waiting alone.
Keloid Formation
Keloids represent the most severe complication from ingrown hair inflammation.
Your keloid genetics and skin of color increase this risk substantially. These raised scars form when your immune system overreacts to shaving trauma.
Keloid location typically affects your neck, jawline, and beard area. Keloid severity varies, but keloid prevention through proper shaving techniques remains your best defense against permanent scar formation.
Hair Loss and Regrowth
Chronic ingrown hairs can permanently damage your hair follicle structure, leading to scarring alopecia and disrupted growth cycles.
Hair miniaturization occurs when follicle regeneration becomes compromised, while hormonal influence affects hair roots’ ability to recover.
Recovery strategies include:
- Gentle scalp massage – stimulates blood flow to hair follicles
- Avoiding further irritation – prevents additional follicular damage
- Using growth-promoting treatments – supports natural hair structure repair
- Managing underlying hormones – addresses root causes of hair loss
- Consulting dermatologists – confirms proper diagnosis and treatment
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can a shave cause ingrown hair?
Yes, shaving definitely causes ingrown hairs.
When you shave, you’re cutting hair at sharp angles that easily pierce back into your skin.
Dull razors, shaving against the grain, and aggressive technique make it worse.
What are ingrown hairs?
Up to 80% of Black men experience razor bumps regularly.
Ingrown hairs occur when your hair grows back into your skin instead of outward, creating those annoying red bumps you’ve probably noticed after shaving.
Can shaving & tweezing cause ingrown hairs?
Absolutely, both shaving and tweezing cut hair below skin level, creating sharp tips that easily pierce back into your skin.
These methods force hair to grow downward instead of outward, triggering inflammation.
What are ingrown hairs & razor bumps?
Ingrown hairs are hairs that grow back into your skin instead of rising up from it.
You’ll recognize them as raised red bumps, also called razor bumps, that can become itchy, painful, or infected.
What causes ingrown hairs on the face?
Facial ingrown hairs develop when you shave too close, cut hair below skin level, or shave against the grain.
Dead skin cells can also trap growing hairs, forcing them to curl back into your skin.
How to prevent ingrown hairs?
Stop shaving, start healing.
Exfoliate daily, shave with the grain using sharp blades, apply warm compresses, and moisturize afterward.
You’ll dodge razor bumps by treating your skin gently and avoiding aggressive hair removal techniques.
How do I stop ingrown hairs after shaving?
Switch to an electric razor or single-blade razor, shave with the grain using short strokes.
Apply warm compresses daily, exfoliate gently, and moisturize afterward to prevent hairs from curling back into your skin, following the concept of shaving with the grain.
Why am I suddenly getting more ingrown hairs?
When it rains, it pours – you’re likely shaving more aggressively, using dull blades, or changed your routine recently.
Hormonal shifts, stress, or new products can also trigger increased ingrown hairs suddenly, which can be a complete concept to understand the sudden change.
What is the fastest way to heal an ingrown hair?
Apply warm compresses for 10-15 minutes to open pores, then gently exfoliate with a washcloth.
Don’t pick or squeeze the bump.
Use antibiotic ointment if infected, and let hair grow naturally.
What causes ingrown hairs if you don’t shave?
Like stubborn guests who won’t leave, ingrown hairs can appear even without shaving.
You’ll get them from plucking, waxing, threading, or wearing tight clothing that forces hair to curl back into your skin instead of growing outward, which can lead to ingrown hairs.
Conclusion
Coincidentally, the same razor that promises smoothness often creates the ingrown hair causes from shaving you’re trying to avoid.
You’ve learned that sharp blades, proper exfoliation, and shaving with the grain can break this cycle.
Your hair texture and genetics play a role, but they don’t determine your fate.
By following these prevention strategies and seeking medical treatment when needed, you’ll transform your shaving routine from a source of frustration into a pathway to healthier, bump-free skin.
- https://dermatology.ca/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Ingrown-Hair-EN-CDA-Patient-Materials.pdf
- https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/i/ingrown-hairs-pseudofolliculitis.html
- https://scholiva.com/articles/ingrown-hair-infections-causes-management/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17722-ingrown-hair
- https://curology.com/blog/how-to-prevent-ingrown-hairs-according-to-the-experts/