This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.
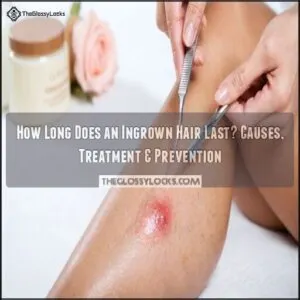 You’ll typically deal with an ingrown hair for 1-2 weeks in mild cases.
You’ll typically deal with an ingrown hair for 1-2 weeks in mild cases.
Without treatment, more severe or infected cases can stick around for up to a month. How long does an ingrown hair last exactly? It depends on your hair type, skin sensitivity, and how quickly you address it.
Curly or coarse hair often leads to longer-lasting ingrown hairs. You can speed healing by gently exfoliating, applying warm compresses, and avoiding further irritation.
Remember that picking at it only prolongs the healing process – sometimes patience truly is the best medicine for those pesky hair rebels.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Ingrown Hair Overview
- How Long Does Ingrown Hair Last
- Factors Affecting Ingrown Hair Duration
- Ingrown Hair Stages and Duration
- Average Duration of Ingrown Hairs
- Treatment Options and Duration
- Preventing Future Ingrown Hairs
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How long do ingrown hairs last?
- What are the causes and symptoms of ingrown hair?
- How long does it take for an infected ingrown hair to clear up?
- How long does it take for ingrown hair to grow out?
- Do ingrown hairs heal on their own?
- What can make ingrown hairs last longer?
- How do you treat infected ingrown hair?
- What happens if an infected ingrown hair goes untreated?
- Should I squeeze an infected ingrown hair?
- What does an infected ingrown hair cyst look like?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Ingrown hairs usually clear up in 1-2 weeks, but severe or untreated cases can last up to a month.
- Curly, coarse hair and sensitive skin tend to cause longer-lasting ingrown hairs.
- Treat ingrown hairs with warm compresses, gentle exfoliation, and antibacterial ointments to speed up healing.
- Don’t pick or squeeze ingrown hairs, as it can lead to infections, scarring, or prolonged healing time.
Ingrown Hair Overview
Ingrown hairs happen when a hair curls back or grows sideways into your skin, causing irritation and sometimes infection.
They’re common in areas you shave or wax, like your legs, face, or bikini line.
Causes and Risk Factors
Beneath your skin, flawed grooming routines and natural tendencies make ingrown hairs almost inevitable.
These painful irritations, ranging from mere nuisances to persistent problems, depend heavily on your hair type and habits.
Here are 5 key causes for ingrown hairs:
- Curly hair naturally curls back into the skin, trapping itself.
- Using poor shaving methods, like shaving against hair growth.
- Clothing friction from tight outfits irritates hair follicles.
- Skin clogging by dead cells blocks hair from growing out.
- Sharp-tipped strands from frequent hair removal pierce the skin.
Your daily choices really influence your ingrown hair timeline.
Common Areas Affected
Ingrown hairs tend to pop up in areas where hair is thicker or frequently removed, causing discomfort and irritation.
Shaving and friction make these spots more prone to trouble:
- Facial hair and neck: Coarse strands in the beard area often grow sideways, leading to long-lasting bumps.
- Legs and bikini line: Leg ingrowns and bikini line bumps are common, especially after shaving or waxing.
- Armpits and pubic region: Moisture and constant friction contribute to stubborn armpit issues and groin irritation.
The ingrown hair timeline varies by location, affecting how long ingrown hairs last.
Shaving against the grain increases this risk, so consider improved shaving techniques.
Symptoms and Signs
How can you tell if you’re dealing with ingrown hair symptoms? Look for an initial bump—a small, raised spot that may itch or feel tender.
As it worsens, you’ll notice swelling, pus formation, and possibly even visible hair trapped beneath the skin.
Here’s a quick guide to recognizing symptoms:
Stage Skin Changes Discomfort Level
Ignoring signs like ingrown hair pain or severe itch can worsen irritation.
Using gentle exfoliation or tweezers can help, but avoid squeezing.
With care, your ingrown hair bump may resolve within two weeks.
How Long Does Ingrown Hair Last
Once you’ve identified an ingrown hair, you’re probably wondering how long it’ll stick around. Typically, an ingrown hair lasts about 1-2 weeks, but without proper care, it may linger much longer.
Here’s a general timeline to track its progress:
- Days 1-3: You’ll notice a red bump forming as the hair curls back into your skin.
- Days 4-7: Inflammation increases, and you may see a lump with pus inside.
- Days 8-14: The hair finally surfaces, leading to gradual healing.
Avoid picking or squeezing to sidestep infection, extended discomfort, or unwanted scars. If left untreated, the issue may persist for weeks. Factors like ingrown hair recovery practices and scarring timeline influence how quickly an ingrown hair resolves. Quick responses reduce pain duration and help the area heal faster.
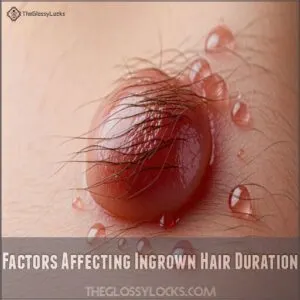
Factors Affecting Ingrown Hair Duration
How long an ingrown hair lasts depends on several factors, like your hair type, skin sensitivity, and where it’s located.
Proper care and timely treatment can speed up healing and reduce irritation.
Hair Type and Texture
Your hair type plays a big role in how long ingrown hairs stick around.
Curly hair and coarse hair are more likely to grow back into the skin due to their natural curl patterns and sharp ends.
Thick hair, with its robust strands, can take a bit longer to grow out properly, while fine hair tends to cause fewer issues since it’s less likely to pierce the skin.
Afro-textured hair, with its tight curls and unique texture, often results in longer healing times.
Hair texture and curvature directly influence how quickly hair escapes the follicle during its growth cycle, and this is a key factor in determining the healing times and how hair types like curly hair affect the skin.
Skin Type and Sensitivity
Your skin type plays a huge role in how long an ingrown hair sticks around.
Sensitive skin often reacts more strongly, with redness and inflammation lasting longer than usual.
If you’ve got dry skin, dead cells build up faster, trapping hairs and stretching the healing process to about 1-2 weeks.
On the other hand, oily skin can intensify inflammation, especially on areas like your face, where pores are more active.
To speed up healing, use non-irritating products that protect your skin’s natural balance.
Moisturizers and gentle skincare routines can go a long way in boosting recovery time and lowering irritation risks.
- **Dry patches slowing you down? Moisturize frequently.
- **Sensitive skin? Handle products and tweezers gently.
- **Irritation-prone areas? Skip harsh scrubbing.
Ingrown Hair Location
Where your ingrown hair appears can influence how long it takes to heal.
Facial Ingrowns and Neck Ingrowns usually disappear faster because of better blood flow and less rubbing.
On the flip side, Pubic Ingrowns might stick around longer due to tight clothes, excess moisture, and coarse hair.
Armpit Ingrowns can be tricky since sweat and bacteria often slow the healing process, increasing the chances of infection.
Leg Ingrowns are typically the least problematic, often needing minimal ingrown hair treatment to heal within a week.
To help your ingrown hair heal, avoid shaving against the grain, wear loose clothing, and exfoliate gently.
Knowing how different areas respond helps you better manage ingrown hair duration and prevent future issues.
Treatment and Self-Care
Recovery hinges on how you care for your skin.
To speed up healing and prevent infection, follow these steps:
- Apply warm compresses (10-15 minutes daily) to soften skin and open hair follicles.
- Use circular exfoliation methods with a washcloth or brush to free trapped hair.
- Dab antibacterial ointments or tea tree oil to stop bacteria growth.
- Soothe irritation with aloe-based or oatmeal-infused lotions.
By sticking to consistent care, ingrown hair treatment becomes easier, ensuring faster healing and healthier skin.
Shaving with the grain can help, as it reduces ingrown hair risks by minimizing irritation, which is a key factor in preventing infection and promoting overall skin well-being.
Ingrown Hair Stages and Duration
An ingrown hair goes through three key stages: inflammation, possible infection, and eventual healing. Understanding these stages can help you manage symptoms and speed up recovery.
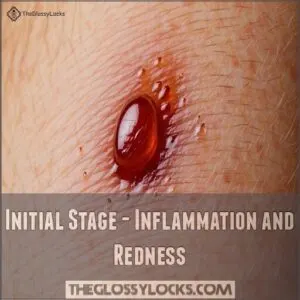
Initial Stage – Inflammation and Redness
Right after hair removal, your body may react by forming a small, irritated ingrown hair bump.
This is the initial stage of ingrown hair inflammation, where you’ll notice early symptoms like redness, mild swelling, and tenderness.
The area might feel warm or sensitive to the touch—your body’s natural defense mechanism kicking in.
This redness extent and mild initial discomfort usually last 1-3 days, with swelling subsiding after 2-3 days.
For those with sensitive skin, these early signs may appear more pronounced.
The redness and irritation are caused by the hair curling back or getting trapped under the skin.
To ease the inflammation, place a warm compress on the affected spot.
This can soothe skin inflammation and reduce discomfort effectively.
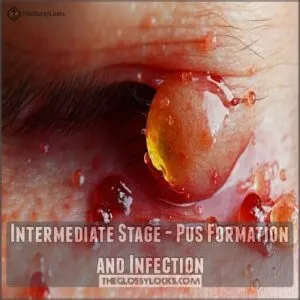
Intermediate Stage – Pus Formation and Infection
As the body fights an infected ingrown hair, pus forms—a mix of white blood cells, bacteria, and dead tissue.
This stage signals infection severity and needs careful attention to prevent spread or scarring.
Here’s what to do:
- Watch for worsening redness, pain, or yellowish-white pus discharge.
- Apply warm compresses for 10-15 minutes to ease inflammation and encourage drainage.
- Gently clean the area with an antiseptic, avoiding squeezing the bump.
- Seek medical help for worsening symptoms or consider antibiotic options if needed.
Advanced Stage – Healing and Resolution
Once the inflammation settles, your skin begins to heal. During the advanced healing stage, you’ll notice redness fading and pain easing within 3-5 days.
Here’s a short, engaging blockquote in the same tone as the content:
As inflammation subsides, your skin enters healing mode—redness fades and discomfort retreats, signaling the path to recovery.
By mid-recovery (days 6-10), swelling reduces, and your follicles start repairing. Full resolution typically happens by day 11-14, but healing time can vary.
Proper care prevents long-term effects like scarring or infection recurrence. Be patient if discoloration lingers—it fades with time.
Without care, scarring treatment might be needed, so focus on keeping the area clean and moisturized. Regular exfoliation can help with beard ingrown hair prevention.
Average Duration of Ingrown Hairs
Ingrown hairs usually last about one to two weeks, depending on the area and how they’re treated.
With proper care, most heal quickly, but infections or irritation can extend the healing time.
Duration of Ingrown Hairs in Different Areas
The duration of ingrown hairs varies depending on the area and factors like skin thickness and friction. Healing times differ, especially for body hair in sensitive or regularly shaved spots.
- Facial Hair Duration: Ingrown hairs on the face, particularly in the beard area, may take 5–10 days to heal with proper care. Coarse hair might take longer.
- Leg Hair Duration: Ingrown hairs on the legs often resolve faster, typically within 3–7 days, due to thinner skin.
- Armpit Hair Duration: Healing can take 7–10 days due to constant movement and rubbing.
- Pubic Hair Duration: These take longer, about 10–14 days, because of sweat and irritation.
Proper care reduces inflammation, helps prevent scarring, and speeds up healing.
Average Time for Ingrown Hairs to Heal
An ingrown hair typically heals in 1-2 weeks, depending on care.
Here’s a quick look at its progression:
| Stage | Timeframe | What Happens |
|---|---|---|
| Early | 1-3 days | Redness and mild swelling |
| Middle | 3-7 days | Hair nears skin’s surface |
| Final | 7-14 days | Skin repairs, clears redness |
Untreated duration can lead to infection length increases, scarring duration, or longer complication timelines.
Factors Influencing Healing Time
Healing time for an ingrown hair depends on several factors, and understanding them can help you tackle the problem faster.
- Infection Severity – An infected ingrown hair takes longer to heal as your body fights bacteria and reduces swelling.
- Skin Hydration – Dry, tight skin slows down recovery and raises the chance of lasting marks.
- Exfoliation Habits – Regular exfoliation can release trapped hairs and prevent further irritation.
- Clothing Friction – Tight clothes cause irritation, making healing take longer.
By addressing these factors, combining proper hair removal techniques with home remedies like warm compresses, you can prevent infected ingrown hairs from overstaying their welcome.
You can also prevent ingrown hairs by using proper shaving techniques.
Treatment Options and Duration
You’ve got plenty of options to treat an ingrown hair, from simple home remedies to medical treatments.
The right approach can ease discomfort and shorten healing time, so it’s worth addressing promptly.
Self-Care and Home Remedies for Ingrown Hairs
Wondering how to tackle an ingrown hair at home? Self-care is your best first step and often speeds things up.
Warm compresses work wonders—apply one for 10-15 minutes daily to open pores and help the hair surface. After this, gentle exfoliation with a washcloth can clear dead skin cells and free trapped hairs. But don’t scrub too hard. Keep it kind to your skin.
Many people find that a quality compress is helpful for effective treatment. Tea tree oil is a favorite home remedy. With natural antibacterial properties, it can reduce the risk of infection. Just dilute it with water before applying.
Another soothing option is oatmeal lotion—it calms irritation and feels great on damp skin. For itching or redness, hydrocortisone cream is a lifesaver.
Here’s a quick guide:
Skip shaving and wear loose clothing to avoid extra friction. Let your skin heal naturally.
Medical Treatment for Infected Ingrown Hairs
If an ingrown hair gets infected, medical treatment can help get things under control quickly.
A healthcare provider might suggest options that work better than at-home remedies, such as:
- Antibiotic options: Creams can treat infection at the site, while pills handle severe infections.
- Steroid use: Reduces redness, itching, and swelling.
- Cyst removal: For stubborn or painful bumps, surgical options promote proper healing.
- Retinoid creams: Remove dead skin cells, prevent scarring, and make future ingrowns less likely.
- Laser therapy: Perfect for reducing recurring ingrown hairs.
Remember, infections can worsen without attention.
When bumps are red, painful, or pus-filled, check with a healthcare provider promptly to prevent complications.
Impact of Treatment on Ingrown Hair Duration
The right ingrown hair treatment can make all the difference.
Effective remedies, like warm compresses or gentle exfoliation, often speed healing in just a few days.
Over-the-counter creams or prescribed medication may reduce infection and improve remedy speed, helping you see results within 2-5 days.
More serious cases might require professional care, cutting the scarring timeline and tackling recurrence risks.
Proper care guarantees hair regrowth happens naturally, minimizing complications.
Whether you’re relying on home remedies or medication, focusing on the follicle is key to faster recovery and fewer future ingrown hair issues.
Preventing Future Ingrown Hairs
You can prevent future ingrown hairs by following proper shaving techniques and adopting good skincare habits. Regular exfoliation, moisturizing, and using alternative hair removal methods can substantially reduce the risk.
Preventing Ingrown Hairs With Proper Shaving Techniques
Now that you understand treatment options, let’s look at prevention. The way you shave can stop razor bumps before they start.
Smart shaving techniques prevent ingrown hairs:
- Prep Your Skin: Wash with warm water for 2-3 minutes to soften hair before shaving.
- Choose the Right Tools: Use a sharp, clean razor type – single-blade often works best.
- Follow Hair Growth: Shave in the direction your hair grows to reduce skin irritation.
- Apply Proper Products: Use quality shaving cream to create a smooth surface for your razor.
- Care After Shaving: Rinse with cool water and apply alcohol-free moisturizer for post-shave care.
These simple shaving techniques can save you weeks of dealing with painful razor bumps. Consider using specialized shaving products for sensitive skin.
Exfoliating to Prevent Ingrown Hairs
Beyond good shaving, regular skin exfoliation clears away dead skin cells that trap hairs.
Choose between exfoliation methods that work best for you—chemical exfoliants (AHAs, BHAs) for sensitive skin or physical scrub types for tougher areas.
Use exfoliation tools like a gentle exfoliating brush in circular motions, focusing on common trouble spots. Understanding different exfoliation products can help you make the right choice.
Maintain an exfoliation frequency of 2-3 times weekly—this prevents clogged follicles without irritating skin. For sensitive skin, start once weekly and increase gradually.
Always complete with post-exfoliation care: apply alcohol-free moisturizer to soothe skin. This simple routine helps prevent ingrown hairs effectively.
Using Alternative Hair Removal Methods
While exfoliation helps, changing your hair removal techniques can stop ingrown hairs before they start.
Laser hair removal offers permanent results by targeting hair follicles directly, though costs vary depending on treatment area. Electrolysis provides similar benefits at a different electrolysis cost point and works well on sensitive skin.
Depilatory creams dissolve hair proteins without creating sharp edges that can pierce skin when regrowing. The waxing benefits include removing hair from the root and, when done regularly, thinner regrowth.
Sugaring works similarly to waxing but is gentler on sensitive skin. For home use, proper epilator usage removes hair from the root but requires careful technique.
These hair removal alternatives prevent ingrown hairs by either permanently reducing hair growth or removing hair without creating the sharp edges that lead to skin penetration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long do ingrown hairs last?
Ingrown hairs can feel like they last forever.
Typically, they resolve within 1-2 weeks with minor irritation.
Without treatment, they may persist longer, especially if infected.
Proper care speeds up healing time.
What are the causes and symptoms of ingrown hair?
Your hair can grow back into your skin when curly strands curl inward or dead skin clogs follicles.
You’ll notice red bumps, itching, and sometimes pus where the trapped hair causes inflammation.
How long does it take for an infected ingrown hair to clear up?
You’ll typically see an infected ingrown hair clear up in 1-2 weeks with proper care.
If you’re using antibiotics, improvement should start within 2-3 days.
Seek medical help if it doesn’t improve.
How long does it take for ingrown hair to grow out?
Those stubborn little hikers under your skin typically take about 1-2 weeks to emerge naturally.
You’ll see faster results if you exfoliate regularly and avoid further irritation by taking a break from shaving.
Do ingrown hairs heal on their own?
Yes, they can heal on their own if left alone, usually within a week or two.
Avoid picking or squeezing them, as this can trigger infection or scarring.
Gentle exfoliation may help speed things up, and it is particularly important to avoid actions that could lead to further issues.
What can make ingrown hairs last longer?
An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
Improper shaving, tight clothing, poor hygiene, or picking at the bumps can trap hairs longer.
Ignoring infections or failing to exfoliate regularly worsens healing and irritation.
How do you treat infected ingrown hair?
Clean the area gently with warm water and soap, then apply an antibiotic ointment to fight infection.
Avoid squeezing or picking.
If it worsens, see a doctor for possible antibiotics or minor surgical removal.
What happens if an infected ingrown hair goes untreated?
Imagine ignoring a small, red bump.
If left untreated, an infected ingrown hair can worsen, leading to pus, scarring, or even serious infections like staph.
It could spread, requiring antibiotics or medical attention to heal.
Should I squeeze an infected ingrown hair?
You shouldn’t squeeze an infected ingrown hair—it can push bacteria deeper, worsen infection, or cause scarring.
Instead, gently clean the area, apply a warm compress, and consider seeing a doctor for proper treatment.
What does an infected ingrown hair cyst look like?
A stitch in time saves nine—spotting an infected ingrown hair cyst early is key.
You’ll notice a swollen, painful bump that’s red, warm, or filled with pus.
It might feel tender and worsen without treatment.
Conclusion
Dealing with an ingrown hair can feel like waiting for rain in a drought—it requires patience.
How long does an ingrown hair last? Usually 1-2 weeks, but severe cases may take up to a month.
Factors like hair type, sensitivity, and treatment practices all play a role.
Gentle care, exfoliating, and avoiding irritation speed recovery. If you notice infection, seek medical advice promptly.
With proper care, you can handle these stubborn bumps effectively and prevent future ones.









Eric White
August 31, 2019 at 06:27 PM
Yeah.. its indeed becomes trouble, when they appeared all we can do is to do keep a safety check and follow the guidelines, thanks for sharing man :)