This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.

Seek shade during peak hours and wear protective clothing. Check your skin monthly for new spots or changes in existing moles. Think of it as your monthly skin inventory check. Smart habits and the right products make all the difference when protecting delicate skin from cancer-causing UV damage.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Why Sensitive Skin Needs Special Protection
- How UV Rays Increase Skin Cancer Risk
- Choosing The Right Sunscreen for Sensitive Skin
- Smart Sun Safety Habits for Sensitive Skin
- Avoiding Indoor Tanning and Artificial UV Sources
- Daily Skin Checks and Early Detection Tips
- When to Visit a Dermatologist
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Choose mineral sunscreens over chemical ones – You’ll avoid irritating ingredients like oxybenzone while getting effective protection from zinc oxide or titanium dioxide that won’t sting your delicate skin.
- Time your sun exposure strategically – You’ll prevent burns by checking the UV Index and staying indoors during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), scheduling outdoor activities for early morning or evening instead.
- Perform monthly skin checks religiously – You’ll catch potential problems early by examining your entire body for new spots, changing moles, or anything that looks different from your baseline.
- Never use tanning beds with sensitive skin – You’re exposing yourself to UV radiation up to 15 times stronger than natural sunlight, dramatically increasing your skin cancer risk while triggering painful reactions.
Why Sensitive Skin Needs Special Protection
If you have sensitive skin, your body’s natural barrier can’t handle harsh chemicals found in many regular sunscreens.
Your skin reacts more strongly to UV damage and needs gentler protection that won’t cause irritation while still preventing cancer.
How Sensitive Skin Reacts to Sun Exposure
In the context of sun exposure, your sensitive skin acts like a canary in a coal mine. UV rays trigger faster reactions than typical skin types experience.
Here’s how sensitive skin types respond to sun exposure:
- Redness appears within minutes – Your skin shows sunburn prevention needs immediately
- Burning happens at lower UV levels – What others tolerate causes UV damage for you
- Recovery takes longer – Photo protection becomes essential for healing
- Reactions vary by season – Winter sun still triggers skin sensitivity responses
- Pain intensifies quickly – Discomfort signals urgent need for sun protection
Common Irritants in Standard Sun Protection
Many standard sunscreens contain chemical filters like oxybenzone that trigger reactions in sensitive skin. Fragrance allergens and preservatives cause redness and burning. Alcohol-based formulas strip natural oils, while PABA concerns affect those with specific sensitivities.
These irritants can make your skin more vulnerable to UVA and UVB damage, defeating the purpose of broad-spectrum sunscreen protection entirely.
How UV Rays Increase Skin Cancer Risk
UV rays from the sun damage your skin cells by breaking down their DNA, which can lead to skin cancer over time.
You’re exposed to these harmful rays year-round, not just during summer, since they reflect off surfaces like snow and water and can reach you even on cloudy days.
Types of UV Radiation and Skin Damage
Understanding radiation exposure becomes critical when you have sensitive skin. The sun emits three types of UV radiation that threaten your skin’s health. UVA rays penetrate deep into your skin, causing long-term damage and premature aging. UVB radiation burns your skin’s surface and directly damages DNA.
- UVA effects include DNA damage deep in skin layers, leading to skin cancer
- UVB damage causes sunburns and surface-level skin lesions that increase cancer risk
- UVC risks are minimal since Earth’s atmosphere blocks most of these rays
- UV radiation creates free radicals that attack healthy skin cells
- Skin cancer develops when accumulated radiation exposure overwhelms your skin’s repair mechanisms
Year-round Dangers of UV Exposure
Don’t get caught off guard by winter weather. Snow reflects up to 80 percent of the sun’s UV light, so the rays hit you twice, creating Seasonal Risks even during cold months.
Both UVA and UVB rays cause Skin Damage year-round, making Daily Protection essential. This UV Reflection doubles your exposure, requiring consistent sun protection regardless of temperature.
Check the UV Index for accurate UV Forecasting.
Choosing The Right Sunscreen for Sensitive Skin
When you’re dealing with sensitive skin, finding the right sunscreen can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. Mineral sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide offer your best protection without the harsh chemicals that can trigger reactions.
Mineral Vs. Chemical Sunscreens Explained
You’ll face two main sunscreen types: mineral and chemical. Mineral sunscreens use zinc oxide or titanium dioxide to create a physical barrier that reflects UV rays. They work immediately and rarely cause skin reactivity.
Chemical sunscreens absorb UVA and UVB rays but can irritate sensitive skin. They contain ingredients like oxybenzone that may trigger reactions.
For sensitive skin, mineral formulas offer safer UV protection. Understanding sunscreen basics is essential for making an informed decision about the right sunscreen for your skin type.
Best Broad-spectrum SPF Options
Top dermatologists consistently recommend mineral sunscreens with SPF 30 or higher for sensitive skin. La Roche-Posay Anthelios and EltaMD Physical are standout choices, offering powerful broad spectrum protection without irritation. These zinc oxide formulas act like armor, shielding delicate skin without stinging or causing breakouts.
Skip chemical sunscreens that can burn. For best results, consider using a broad spectrum sunscreen tailored to your skin type.
Smart Sun Safety Habits for Sensitive Skin
You’ll need smart strategies that work with your skin’s unique needs to stay protected without causing irritation.
Building the right sun safety habits means timing your activities and choosing protection that won’t trigger reactions.
Seeking Shade and Planning Outdoor Activities
Smart shade planning makes all the difference for sensitive skin. Check UV forecasts before heading outdoors and schedule activities for early morning or evening when UV radiation protection needs are lower.
Shade structures like umbrellas and pavilions become your best friends during peak hours. Plan daily planning around the UV Index – your skin will thank you later.
Wearing Protective Clothing and Accessories
Your skin’s defense starts with smart clothing choices. Build your UV armor with these essentials:
- Sunglasses – Block 99% UVA and UVB rays
- Hats and Headwear – Wide brims shade face and neck
- Protective Gloves – Shield hands during gardening
- Face Masks – Cover cheeks and nose outdoors
- Scarf Protection – Wrap neck and shoulders
Choose tightly-woven fabrics for maximum sun protection methods. Additionally, understanding sunscreen lotion benefits can bolster your skin’s natural defenses.
Using UV Index Forecasts for Protection
Your smartphone’s weather app holds a secret weapon for sensitive skin protection. The UV Index forecast tells you exactly when UV rays will peak each day. **Plan outdoor activities before 10 a.m. or after 4 p.m.
** when UV radiation drops. Check daily forecasts to adjust your sunscreen application and sun safety measures accordingly. Understanding daily sun protection methods is essential for preventing skin cancer and maintaining healthy skin.
| UV Index Level | Protection Needed |
|---|---|
| 0-2 (Low) | Minimal sunscreen for extended outdoor time |
| 3-5 (Moderate) | SPF 30+ sunscreen, seek shade midday |
| 6-7 (High) | SPF 30+, protective clothing, limit sun exposure |
| 8-10 (Very High) | Maximum protection, avoid midday sun |
| 11+ (Extreme) | Stay indoors during peak hours |
Avoiding Indoor Tanning and Artificial UV Sources
If you have sensitive skin, tanning beds are your worst enemy because they blast concentrated UV rays that can irritate and damage your skin faster than natural sunlight.
You’ll get better results with safer alternatives like self-tanning products or bronzing makeup that won’t put your skin at risk for cancer or painful reactions.
Risks of Tanning Beds for Sensitive Skin
Tanning beds bombard your already vulnerable skin with concentrated UV radiation that’s up to 15 times stronger than midday sun. This artificial UV exposure dramatically increases skin cancer risk while triggering immediate reactions like burning, redness, and painful inflammation.
Your sensitive skin lacks the natural defenses to handle these Indoor Tanning Hazards, making each session a gamble with your health.
Safer Alternatives to Tanning
When you’re craving that sun-kissed look, consider these UV-free tanning alternatives that won’t irritate sensitive skin:
- Self-tanning lotions with DHA create gradual color without UV rays or sunlamps
- Spray tanning offers even coverage using hypoallergenic, fragrance-free formulas
- Makeup bronzers provide instant, removable natural glow
- Gradual tanners let you build color slowly while monitoring sensitivity
Skip tanning pills—they’re unsafe. Always patch test first and choose broad-spectrum SPF protection outdoors.
For a safe and healthy glow, it’s vital to research sensitive skin tips before trying any new tanning method.
Daily Skin Checks and Early Detection Tips
You’ll become your own skin detective with monthly self-exams that catch changes before they become serious problems.
Think of it like checking your car’s oil – a simple routine that prevents major trouble down the road.
How to Perform Monthly Self-exams
Regular self-exams help you catch skin cancer early when treatment works best. Pick a day each month to check your entire body from head to toe using a mirror. Look for new spots or changes in existing moles. Use this systematic approach:
| Body Area | Self Exam Tips |
|---|---|
| Face & Scalp | Use handheld mirror, check behind ears |
| Arms & Hands | Examine palms, between fingers, under nails |
| Torso & Back | Use full-length mirror, ask partner to help |
| Legs & Feet | Check soles, between toes, back of legs |
| Skin Mapping | Take photos for mole tracking over time |
Dermatologist guidance recommends checking spots that feel different, look unusual, or won’t heal. Cancer screening at home isn’t perfect, but it’s your first line of defense against melanoma and other skin damage.
Warning Signs to Watch for on Sensitive Skin
Look for skin lesions that change shape, size, or color. Red spots that don’t heal within two weeks need attention. Itchy patches on sensitive skin might signal trouble, especially after sun exposure. New moles appearing after age 30 raise concern. Watch for discoloration around existing moles.
These warning signs help catch skin cancer early, including melanoma. Regular skin cancer screenings are essential for identifying potential skin issues early on.
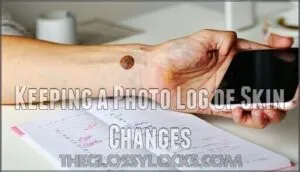
Keeping a Photo Log of Skin Changes
Take photos of suspicious spots with your smartphone’s camera. Create a digital archiving system by photographing moles from the same angle monthly. This photo diary helps with change detection since memory isn’t reliable.
Compare images side-by-side to spot subtle differences. Your dermatologist can review these skin tracking records during visits, making mole monitoring more effective for melanoma prevention.
When to Visit a Dermatologist
You’ll know it’s time to see a dermatologist when you spot new growths, moles that change color or size, or spots that won’t heal after a few weeks.
Think of your dermatologist as your skin’s best friend—they can catch problems early and help you create a prevention plan that works with your sensitive skin.
What Symptoms Require Expert Evaluation
Your sensitive skin needs immediate attention when you spot new growths, mole changes, or abnormal pigmentation. Watch for skin lesions that bleed, itch, or don’t heal within weeks. Itchy patches that persist despite treatment warrant evaluation.
Any mole displaying irregular borders, multiple colors, or rapid growth requires professional assessment for melanoma, basal cell, or squamous cell skin cancer. Understanding sensitive skin care is vital for identifying potential skin issues early on.
How Dermatologists Support Prevention and Care
Beyond annual skin cancer screening, dermatologists provide customized treatment plans adapted to your skin’s unique needs. They’ll recommend the best broad-spectrum sunscreen and SPF levels for your sensitive skin type.
Their medical support includes monitoring suspicious spots, providing preventive care guidance, and catching problems early. **Think of dermatologist guidance as your skin’s best defense system against cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can sensitive skin develop tolerance to sun exposure?
Like a garden that wilts under harsh sunlight, your delicate skin can’t build armor against UV rays. You won’t develop tolerance – sensitivity actually increases with damage over time, making protection even more essential.
Are there specific diets that help protect sensitive skin?
You can boost your skin’s natural defenses with antioxidant-rich foods like berries, leafy greens, and colorful vegetables. Omega-3 fatty acids from salmon and mackerel act like internal moisturizers.
How does pollution affect sensitive skins cancer vulnerability?
Pollution creates a double threat for your delicate skin. Air pollutants team up with UV radiation to trigger inflammation and accelerate aging, making you more vulnerable to cancer-causing damage than clean-air dwellers.
Can sensitive skin safely use retinoids for prevention?
Yes, you can use retinoids safely with sensitive skin. Start with cream-based formulas that are gentler and less drying. Begin slowly and consult your dermatologist for proper guidance.
Conclusion
Protecting your sensitive skin means choosing gentle products, seeking shade, and staying vigilant. You’ve learned that mineral sunscreens work better than chemical ones for delicate skin.
You know to check your skin monthly and recognize warning signs. Remember that effective skin cancer prevention for sensitive skin doesn’t require harsh products or complicated routines.
Simple, consistent habits protect you best. Your skin deserves gentle care that actually works.
- https://healthcare.utah.edu/healthfeed/2025/06/steps-prevent-skin-cancer
- https://camelbackderm.com/2025/05/19/uncommon-but-essential-skin-cancer-prevention-tips-you-havent-heard-before/
- https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/prevent/how
- https://www.cnn.com/2025/05/20/health/2025-safest-sunscreens-wellness
- https://www.sunsetpools-spas.com/blog/latest-research-safe-effective-sunscreens-2025